Jaw crusher wear plates represent one of the most critical components in modern crushing operations, directly determining the efficiency, productivity, and profitability of mining, quarrying, and aggregate processing facilities. These specialized components endure extreme compressive forces and constant contact with abrasive materials, making their selection, maintenance, and replacement essential for optimal operational performance. As the global jaw crushers market continues to expand—valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2024 with a projected compound annual growth rate of 4.2% through 2034—understanding the intricacies of jaw crusher wear plates has become increasingly important for equipment operators, maintenance managers, and procurement specialists.
Jaw crusher wear plates consist of two primary components: the fixed jaw (stationary plate) and the movable jaw (swing jaw), both engineered to withstand the intense mechanical stresses inherent in mineral and aggregate crushing processes. The performance of these wear plates fundamentally impacts production capacity, product quality, energy consumption, and overall equipment maintenance costs. This comprehensive guide explores every essential aspect of jaw crusher wear plates, from material composition and design specifications to maintenance best practices and cost optimization strategies.
Jaw crusher wear plates, commonly referred to as jaw dies or jaw liners, are the wearing surfaces that directly contact the material being crushed within the crushing chamber. Unlike structural components that provide equipment support, these plates absorb the primary mechanical stress and material contact, progressively wearing down through the crushing cycle. Their fundamental role is to reduce large rock and mineral fragments to smaller, more manageable sizes through a combination of compression and impact forces.
The jaw crusher operates through a simple but powerful principle: the movable jaw performs a reciprocal motion against the fixed jaw, creating a compression force that breaks down material. This reciprocal action occurs typically 250-400 times per minute, depending on operating parameters and material characteristics. During each compression cycle, wear plates experience tremendous compressive loads, ranging from several hundred to thousands of kilonewtons per minute, applied across their wearing surfaces.
The effectiveness of jaw crusher wear plates extends beyond simple particle size reduction. High-quality plates influence multiple operational aspects: they determine the final product's particle shape and gradation, affect the energy efficiency of the crushing process, and significantly impact the crusher's production capacity. A well-selected wear plate enhances crushing efficiency by up to 30%, while poorly chosen plates lead to increased energy consumption, reduced throughput, and accelerated equipment deterioration.
The material composition of jaw crusher wear plates fundamentally determines their performance characteristics, including wear resistance, impact strength, and operational lifespan. Modern wear plate manufacturing employs several primary material categories, each optimized for specific crushing applications and material types.
High-manganese steel remains the most widely utilized material for jaw crusher wear plates, particularly for hard rock applications. This material category includes several specific grades, with manganese content typically ranging from 12% to 24%, supplemented with chromium and other alloying elements to enhance performance characteristics. The three primary grades are Mn13Cr2, Mn18Cr2, and Mn22Cr2, each offering distinct advantages within specific operational contexts.
Mn13Cr2 (12% Manganese, 2% Chromium): This entry-level high-manganese steel provides moderate wear resistance suitable for softer materials like limestone and certain aggregates. Operating lifespan typically ranges from 400 to 600 hours in soft rock applications, extending to 4,000-6,000 hours in favorable conditions. The material offers cost-effective performance for operations with lower crushing intensity or less abrasive feed materials.
Mn18Cr2 (18% Manganese, 2% Chromium): Positioned as the mid-range option, Mn18Cr2 delivers superior wear resistance and impact strength compared to lower-grade alternatives. This material demonstrates exceptional performance in granite and moderately hard rock crushing, achieving 8,000-12,000 hours of operational lifespan. Operators consistently report 30-40% longer wear life compared to Mn13Cr2, making it the preferred choice for mainstream crushing operations.
For the most extreme crushing applications—particularly recycled concrete, mixed demolition waste, and materials containing metal contaminants—tungsten carbide coatings or composite materials offer exceptional performance. Tungsten carbide wear plates demonstrate 100% improved wear resistance compared to standard manganese steel, extending operational lifespans to 11,000+ hours even in severe applications. However, the significantly higher material and manufacturing costs necessitate careful economic analysis to ensure justified return on investment.

Operating lifespan comparison of different jaw crusher wear plate materials for hard and soft rock applications
Straight Pattern: The simplest design featuring parallel grinding surfaces. Straight plates excel in preliminary crushing stages and softer material processing but provide less aggressive material grip compared to patterned alternatives.
Corrugated Pattern (C): Features regular parallel grooves or ribs, providing enhanced material grip and improved particle shape without excessive aggressiveness. This versatile design works well across most rock types and represents a balanced choice between performance and cost.
Coarse Corrugated Pattern (CC): Features wider, deeper grooves than standard corrugation, offering maximum material grip and aggressive crushing action. Ideal for hard, dense materials requiring forceful compression, though production of finer materials increases slightly.
Quarry Style Pattern: A specialty design optimized for natural quarrying operations, featuring aggressive tooth-like formations for maximum crushing force and particle shape control. This pattern excels in primary crushing stages with large input feed sizes.
Sharp Teeth (ST) and Heavy Duty (UT) Patterns: Ultra-aggressive designs for the most demanding applications, featuring pronounced tooth geometry. These patterns provide maximum crushing efficiency but generate higher particle fines and require careful feed material control to prevent equipment damage.
The operational lifespan of jaw crusher wear plates depends on multiple interconnected variables, ranging from material characteristics to operational parameters and maintenance practices. Understanding these factors enables operators to extend component life and optimize maintenance scheduling.
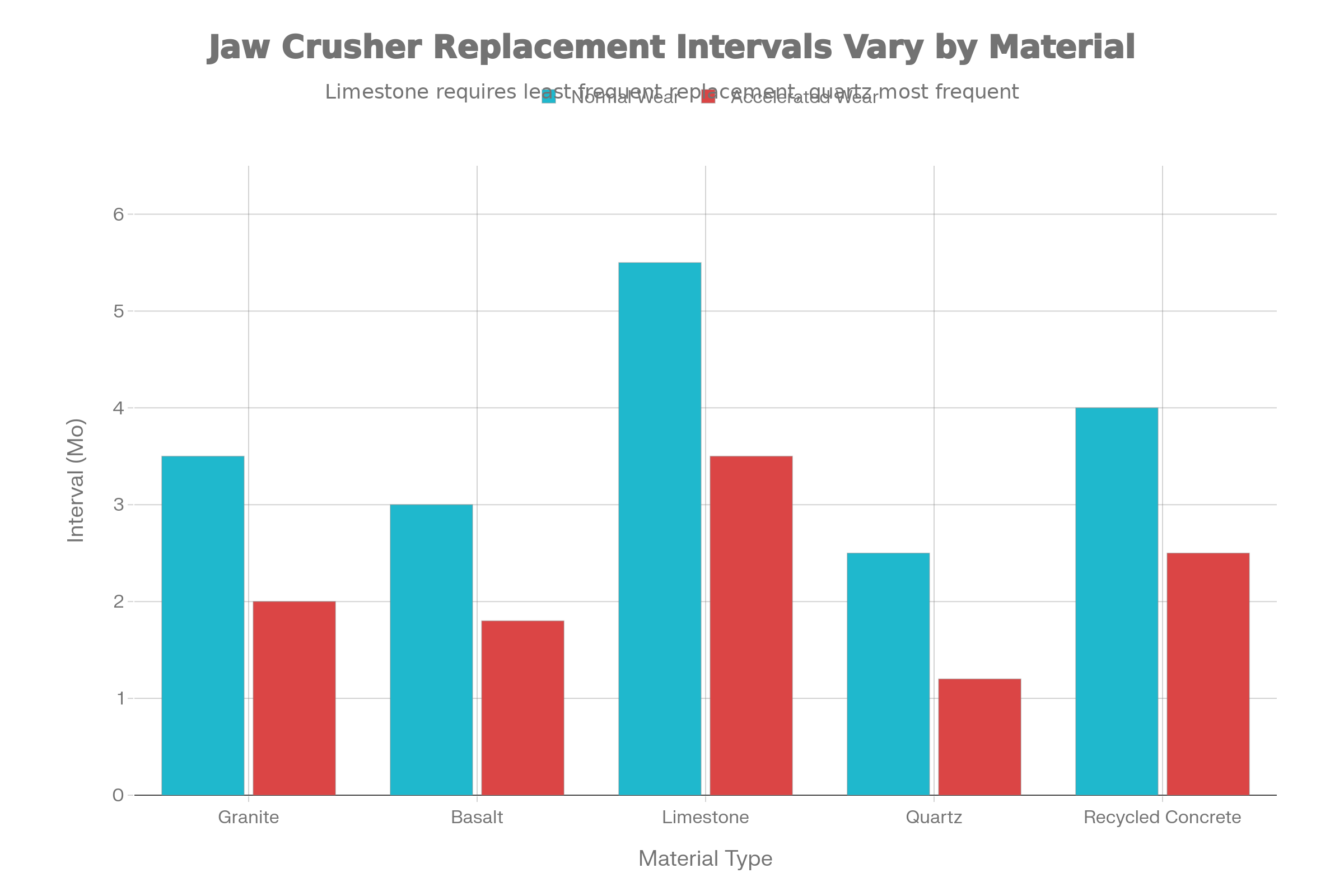
Typical replacement intervals for jaw crusher wear plates based on material hardness and operating conditions
Material Characteristics: The inherent wear resistance of selected material compositions establishes the theoretical performance ceiling. High-manganese steel variants provide 500-1,000 hours in granite applications versus 100-200 hours for budget alternatives, representing five to ten-fold lifespan differences. Material selection, therefore, establishes fundamental operational parameters affecting all subsequent maintenance planning.
Rock Type and Abrasiveness: The specific minerals being processed exert enormous influence on wear rates. Quartz-rich materials like granite and basalt accelerate wear significantly compared to limestone or soft aggregates. Recycled concrete and demolition waste containing steel reinforcement create additional complicating factors, potentially reducing wear plate lifespan by 50% or more.
Operating Parameters: Crusher operating speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), directly correlates with wear progression. Soft material crushing at 350-400 RPM generates different wear patterns than hard material crushing at 250-300 RPM. Similarly, the closed-side setting (CSS)—the minimum outlet gap between jaws—influences wear distribution. A tighter CSS increases compression force, accelerating wear, while a more open setting reduces wear but produces larger product sizes.
Feed Material Management: Proper material feeding represents one of the most significant operational variables influencing wear plate lifespan. Even distribution across the crushing chamber prevents localized wear concentration. Lateral feeding or concentrated material delivery to specific points causes uneven wear, potentially reducing plate life by 30-40% compared to optimally distributed feeding.
Maintenance Practices: Regular inspection, timely plate rotation, effective lubrication, and prompt replacement of worn components extend operational lifespan substantially. Operators implementing comprehensive maintenance programs routinely achieve 50% longer component life compared to those performing only reactive maintenance.
Establishing appropriate replacement intervals represents critical operational management, balancing equipment reliability against maintenance costs. Industry standards provide empirical guidance, though specific applications require customization based on actual operational conditions.
For granite crushing under normal operating conditions, jaw plate replacement intervals typically range from three to four months. Basalt and similarly hard materials generally require replacement every 2.5-3 months under intensive operation. Softer materials like limestone permit longer intervals, averaging 5-6 months between replacement cycles. However, these figures represent general guidelines; actual intervals vary based on specific operational factors.
Operators should monitor several key wear indicators to determine optimal replacement timing:
Thickness Reduction: Jaw plates should be replaced when total thickness diminishes to approximately 25-50mm, depending on specific crusher design and manufacturing specifications. Measurement consistency prevents over-replacement while ensuring safety margins.
Visible Damage: Cracks, deep chipping, or deformation indicate immediate replacement needs, regardless of remaining material thickness. Progressive crack propagation can lead to catastrophic plate failure with attendant safety and equipment damage consequences.
Performance Degradation: Production output decline of more than 15-20% under consistent feeding conditions signals advancing wear. Similarly, flaky particles exceeding 25% of the final product or excessive material buildup within the crushing chamber indicates deteriorating plate condition.
Jaw Plate Rotation: Many modern designs permit jaw plate reversal, allowing crushing on previously unused surfaces. Operators should rotate plates at intermediate wear stages, potentially extending component life by 50% when wear patterns permit reversal use.
| Component Name | Main Function | Importance/Impact of Wear |
| Jaw Plates | Crush material | Affects product size, throughput, and power consumption |
| Liner Plates (Cheek Plates) | Protect main frame sides | Protects structural integrity, affects material flow |
| Bearings | Support eccentric shaft | Essential for smooth operation; wear leads to overheating and failure |
| Toggle Plate | Force transmission and safety | Critical for safe operation; wear affects reliability |
Selecting jaw crusher wear plates based solely on initial purchase cost represents a fundamental economic miscalculation. Total cost of ownership calculations incorporating replacement frequency, downtime expenses, and operational efficiency demonstrate substantially different economics.
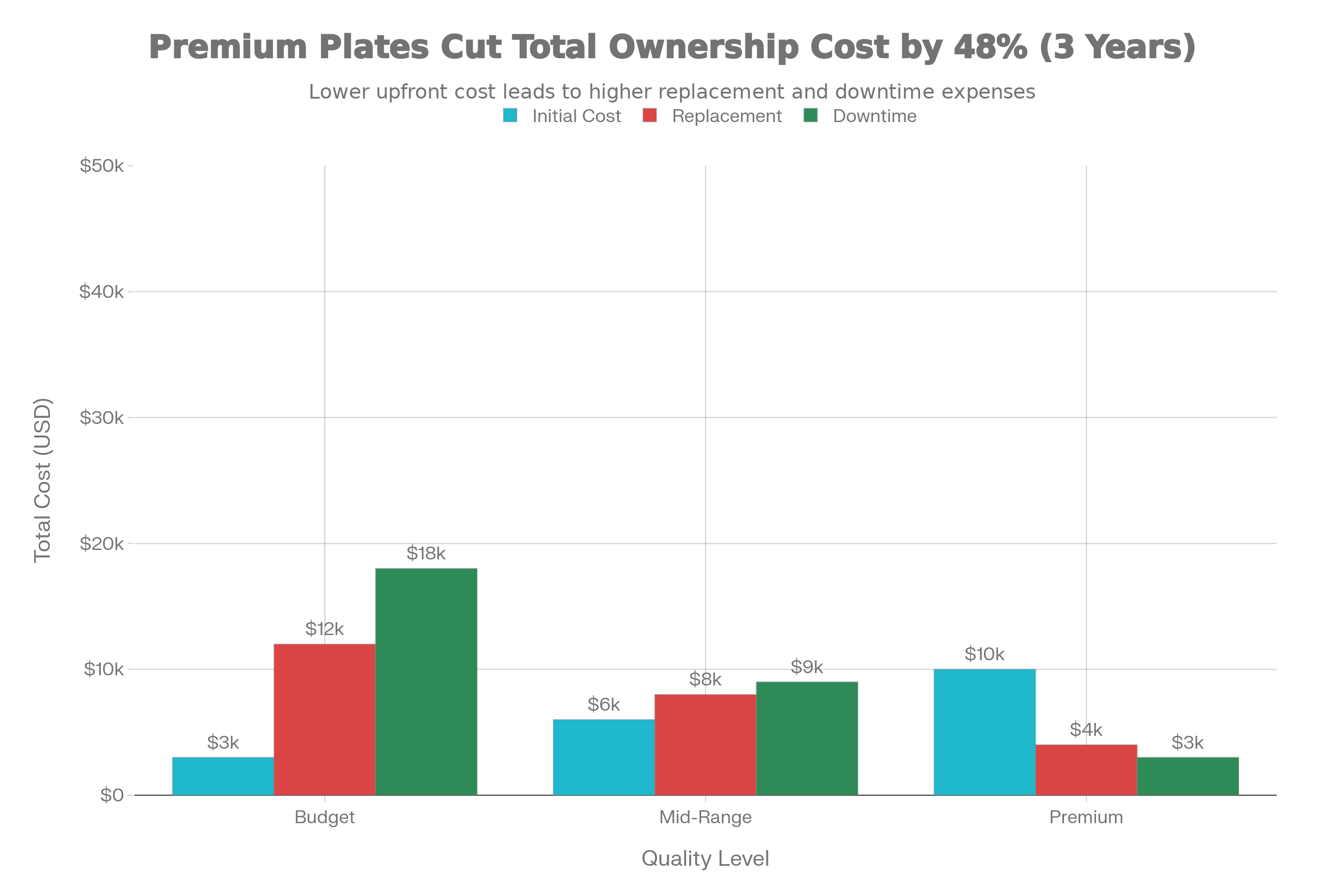
Total cost of ownership comparison for different jaw crusher wear plate quality levels over three years
Budget-quality wear plates, typically manufactured from lower-grade manganese steel or equivalent materials, offer the lowest initial investment—approximately $3,000-5,000 per set. However, rapid wear necessitates replacement every 2-3 months, with estimated three-year replacement costs reaching $12,000-15,000. Production downtime during replacement cycles, combined with efficiency losses from progressive wear, adds additional costs of $15,000-20,000 over three years. The total three-year cost of ownership frequently reaches $30,000-40,000 or higher.
Mid-range standard-quality plates represent a balanced approach, with initial costs of $6,000-8,000 and replacement intervals extending to 3-4 months. Three-year replacement costs approximate $8,000-10,000, while downtime and efficiency-related costs remain moderate at $8,000-12,000, yielding total ownership costs around $22,000-30,000.
Premium high-quality wear plates, manufactured from optimized Mn18Cr2 or superior materials, command initial investments of $10,000-15,000 but deliver exceptional value through extended 4-6 month replacement intervals. Three-year replacement costs remain minimal at $3,000-5,000, while reduced downtime and maintained efficiency eliminate $10,000-15,000 in indirect costs. Total three-year ownership costs approximate $15,000-25,000, representing 30-50% savings compared to budget alternatives despite higher initial investment.
The economic analysis clearly demonstrates that premium quality wear plates justify their higher initial cost through dramatically reduced total cost of ownership, making them the preferred option for continuous production operations where equipment reliability and productivity directly impact profitability.
Optimal jaw crusher performance requires understanding the relationship between crushing ratio, wear plate characteristics, and operational parameters. The crushing ratio—the proportional reduction of feed size to product size—fundamentally affects both efficiency and wear characteristics.
Hard materials including granite, basalt, and quartz benefit from crushing ratios of 6:1 to 8:1, meaning feed material approximately 6-8 times larger than the target output size. These ratios prevent overloading while maintaining productive compression forces. Lower ratios increase wear but provide minimal productivity gains, while higher ratios exceed crushing chamber capacity and cause equipment damage.
Softer materials including limestone and aggregates tolerate higher crushing ratios of 8:1 to 10:1, improving production throughput while maintaining reasonable wear rates. However, even soft materials require parameter management to prevent premature equipment deterioration.
Weekly Visual Inspections: Operators should visually examine jaw plates for visible damage, material buildup, or operational anomalies. Early detection of cracks or chipping permits planned replacement before catastrophic failure occurs.
Monthly Thickness Measurement: Using precision calipers or ultrasonic measurement tools, operators track progressive wear, establishing reliable replacement timing based on actual wear rates rather than theoretical schedules.
Quarterly Plate Rotation: When feasible, rotating jaw plates between fixed and movable jaw positions distributes wear more evenly, extending operational lifespan by 30-50% compared to continuous use in single positions.
Comprehensive Equipment Lubrication: Proper bearing and eccentric shaft lubrication reduces friction-induced wear and heat generation. Manufacturers typically specify lubrication intervals and fluid specifications; adherence to these guidelines prevents premature bearing and seal failures.
Controlled Feeding: Distributing material evenly across the crushing chamber width prevents localized wear concentration. Automatic feed systems with controlled rate management optimize this parameter superior to manual feeding.
Avoid Material Contamination: Oversized feed materials, metal contaminants, or foreign objects cause impact damage and premature plate failure. Implementing feed screening systems protects equipment investment and maintains operational reliability.
Monitor Operating Parameters: Vibration sensors and acoustic monitoring systems detect developing problems before they manifest as catastrophic failures. Modern equipment increasingly incorporates real-time monitoring with automatic shutdown when critical parameters are exceeded.
Dust Suppression: Effective dust control reduces abrasive particle accumulation within the crushing chamber, which accelerates wear through secondary friction. Water spray systems or other dust suppression methods prove highly effective cost-reduction strategies.
Jaw crusher wear plates serve diverse industrial sectors, each with specific application requirements and operational parameters. Understanding these applications provides context for wear plate selection and performance expectations.
Mining Operations: Precious metals, base metals, and mineral extraction represent major jaw crusher applications, processing ores ranging from relatively soft to extremely hard, with operational priorities emphasizing high throughput and product uniformity.
Mining operations typically operate crushers 12-24 hours daily, demanding robust wear plate designs and aggressive replacement scheduling.
Aggregate and Quarrying: Natural stone extraction and aggregate production represent substantial jaw crusher applications, processing materials including granite, limestone, and basalt. These operations prioritize product size consistency and quality, requiring careful wear plate pattern selection and regular maintenance.
Construction and Demolition: Recycled concrete and demolition waste crushing creates extreme challenges for wear plates due to steel reinforcement contamination and varied material hardness. Operators require premium wear plate materials and frequent replacement intervals to manage these demanding applications.
Cement and Industrial Minerals: Limestone crushing for cement production and industrial mineral processing employ jaw crushers for primary and secondary crushing stages. These high-volume operations justify investment in premium equipment and wear components to maximize production continuity.
The global jaw crusher market demonstrates consistent growth, with the market valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2024 and projected to expand at a 4.2% compound annual growth rate through 2034. This expansion reflects increased infrastructure investment in developing economies, rising mineral extraction demand, and growing recycled material processing requirements. The Asia Pacific region, in particular, is experiencing significant market growth due to rapid economic development and increased mining activities.
Technological advancement increasingly influences wear plate development. Modern materials incorporating advanced metallurgical compositions and manufacturing techniques continue to improve performance characteristics. Similarly, digital monitoring systems enabling predictive maintenance scheduling represent significant operational improvements, permitting wear plate replacement optimization based on actual wear progression rather than predetermined schedules.
Sustainable manufacturing practices increasingly influence wear plate production, with manufacturers investing in environmentally responsible casting processes and recycled material incorporation where technically feasible. These developments align with global sustainability initiatives while maintaining performance standards required for demanding industrial applications.
Equipment operators face important decisions regarding wear plate sourcing, with significant implications for cost, compatibility, and performance. Understanding the distinctions between original equipment manufacturer (OEM) and aftermarket options informs strategic procurement decisions.
Original equipment manufacturer wear plates, produced by major equipment manufacturers including Metso, Sandvik, FL Smidth, and ThyssenKrupp, maintain guaranteed compatibility with specific crusher models and incorporate design specifications matching original equipment. OEM plates typically command premium pricing, reflecting manufacturing quality standards and brand positioning. For critical operations where equipment downtime creates substantial economic consequences, OEM sourcing provides important reliability assurance.
Specialized aftermarket suppliers including manufacturers in Asia, Europe, and North America offer wear plates compatible with multiple crusher models at price points typically 20-40% below OEM equivalents. Reputable aftermarket suppliers maintain rigorous quality standards comparable to OEM products, though quality variations exist among different suppliers. Operator reviews, performance metrics, and supplier reputation assessment help identify reliable aftermarket sources offering optimal value.
Many sophisticated operators maintain mixed sourcing strategies, utilizing OEM plates for critical applications while leveraging quality aftermarket options for less-demanding operations, balancing cost optimization against reliability requirements.
Established manufacturers like Haitian Heavy Industry offer comprehensive wear plate solutions backed by over 20 years of foundry expertise and advanced manufacturing capabilities. Operating from a 35,000 square meter facility with an annual production capacity of 80,000 tons, Haitian combines technical sophistication with cost-effective manufacturing for reliable jaw crusher wear plate solutions. The company's ISO 9001 quality management certification, professional technical team, and innovative 3D sand mold printing technology—which shortened new product development cycles to just 2 weeks—provide confidence in product quality and manufacturing reliability.
For equipment operators and procurement specialists evaluating wear plate sourcing options, visiting https://www.htwearparts.com/ provides comprehensive product information, technical specifications, and qualification details supporting informed purchasing decisions aligned with specific operational requirements.
Selecting jaw crusher wear plates from qualified manufacturers incorporating appropriate quality assurance protocols protects operational interests and ensures reliable performance. Recommended manufacturer evaluation includes:
Testing and Analysis: Manufacturers should provide material composition verification through chemical analysis, hardness testing documentation, and metallurgical evaluation confirming material properties match specifications.
Design Engineering: Quality manufacturers maintain technical design capabilities, offering customized solutions for specific applications while maintaining engineering principles supporting reliable performance.
Customer References: Verifiable customer installations, performance documentation, and operator testimonials provide practical validation of claimed performance characteristics.
Emerging technologies increasingly influence jaw crusher wear plate management strategies. Real-time monitoring systems incorporating vibration sensors, acoustic analysis, and wear detection algorithms enable predictive maintenance approaches, replacing traditional time-based replacement schedules with actual condition-based strategies.
These advanced systems detect developing wear patterns, material composition changes, and operational anomalies before they manifest as catastrophic failures. Predictive maintenance capabilities reduce unexpected downtime, optimize replacement timing to balance productivity against maintenance costs, and potentially extend equipment lifespan through early intervention strategies.
Equipment managers considering technology investments should evaluate monitoring system compatibility with existing crusher models and assess integration capabilities with operational information systems. As monitoring technology maturity and cost-effectiveness improve, adoption rates are expected to accelerate, particularly within large-scale mining and aggregate operations where equipment reliability directly impacts profitability.
Jaw crusher wear plates represent critical equipment components profoundly influencing operational efficiency, production reliability, and total cost of ownership across mining, quarrying, aggregate processing, and industrial mineral crushing operations. Successful wear plate selection requires comprehensive understanding of material characteristics, design considerations, operational parameters, and maintenance requirements.
High-manganese steel materials, particularly Mn18Cr2 and Mn22Cr2 compositions, continue delivering superior performance for mainstream crushing applications, while specialized materials including tungsten carbide address extreme operational challenges. Premium quality wear plates, despite higher initial costs, justify their investment through reduced replacement frequency, minimized downtime, and maintained operational efficiency—delivering 30-50% total cost of ownership advantages compared to budget alternatives.
Implementing comprehensive maintenance protocols, monitoring operational parameters, controlling feeding practices, and maintaining preventive inspection schedules extend wear plate lifespan substantially while supporting consistent, reliable equipment performance. Understanding specific application requirements, material characteristics, and operational best practices enables informed decisions optimizing both short-term operational performance and long-term economic outcomes.