The jaw crusher plate is the most frequently replaced wear component in any crushing operation. Poor selection leads to accelerated wear, excessive downtime, reduced productivity, and ultimately, higher total cost of ownership. Conversely, strategic plate selection extends service life by 30–50%, improves product quality, and demonstrates why finding a reliable and cost-effective jaw crusher plate manufacturer requires an understanding of technical specifications beyond unit price alone.
Every jaw crusher operates with a paired system of jaw plates that work in concert to break material:
Positioned vertically on the stationary jaw
Remain immobile during operation
Act as the anvil against which material is compressed
Typically experience lower stress concentrations than moving plates
Can be designed with different material compositions to optimize lifetime
Attached to the reciprocating jaw mechanism
Move back and forth through 20–30° angles
Deliver dynamic compressive force against the fixed jaw
Experience higher impact stresses and wear rates
Often require more frequent replacement than fixed plates
| Alloy Type | Manganese Content | Hardness Range (BHN) | Best For |
| Mn13Cr2 | 13% manganese, 2% chromium | 230 BHN (initial) → 400 BHN (work-hardened) | Soft materials (limestone, coal), low AI materials |
| Mn18Cr2 | 18% manganese, 2% chromium | 240 BHN (initial) → 420 BHN (work-hardened) | Most stone types, standard quarry applications, medium AI |
| Mn22Cr2 | 22% manganese, 2% chromium | 250 BHN (initial) → 450 BHN (work-hardened) | Extremely hard, abrasive materials (granite, basalt, taconite) |
High manganese steel exhibits austenitic properties, meaning it hardens progressively under impact stress rather than becoming brittle. This work-hardening capability represents the fundamental advantage of quality manganese steel—as crushing pressures compress the material surface, hardness increases from initial BHN 230 to operational hardness of 400+ BHN, creating a self-protective layer that extends service life.
Premium cheap jaw crusher plate manufacturers enhance base manganese compositions by adding chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, or titanium. These alloy modifications improve:
Impact toughness during hard rock crushing
Resistance to thermal cycling stress
Durability in abrasive material applications
Work-hardening rate under operational pressures
Selecting the correct alloy requires understanding your feed material's Abrasion Index (AI), a scientific metric indicating how aggressively material particles wear down crushing surfaces.
| Classification | AI Range | French Abrasiveness (G/Ton) | Example Materials |
| Non-Abrasive | 0.0–0.1 | 0–100 | Clay, soft limestone, coal |
| Slightly Abrasive | 0.1–0.4 | 100–600 | Soft limestone, gypsum, shale |
| Medium Abrasive | 0.4–0.6 | 600–1,200 | Most common aggregates, river stone |
| Abrasive | 0.6–0.8 | 1,200–1,700 | Granite, basalt, ironstone |
| Very Abrasive | 0.8+ | 1,700+ | Quartzite, taconite, recycled concrete |
Recommended Alloy: Mn13Cr2, standard teeth or wide tooth design. Rationale: Lower abrasion indexes don't require maximum hardness; Mn13Cr2 provides cost efficiency while delivering adequate wear resistance for low-stress applications. Expected service life: 8,000–12,000 operating hours.
Recommended Alloy: Mn18Cr2 (standard specification), corrugated or coarse corrugated design. Rationale: Mn18Cr2 represents the industry-standard sweet spot, balancing toughness and hardness for 80% of global crushing operations. Superior work-hardening capability extends plate lifetime while maintaining competitive pricing. Expected service life: 12,000–18,000 operating hours.
Recommended Alloy: Mn18Cr2 or Mn22Cr2, sharp teeth or heavy-duty design. Rationale: Hard rock abrasion accelerates surface wear; premium alloys with enhanced chromium content resist particle embedding and maintain crushing efficiency longer. Expected service life: 15,000–22,000 operating hours.
Recommended Alloy: Mn22Cr2 or specialized ultra-thick configurations, heavy-duty ultra-thick (UT) profiles. Rationale: Extremely abrasive materials demand maximum hardness and thickness; ultra-thick configurations reduce replacement frequency from every 6–8 months to 12–15 months, offsetting premium pricing through extended operational periods. Expected service life: 18,000–28,000+ operating hours.
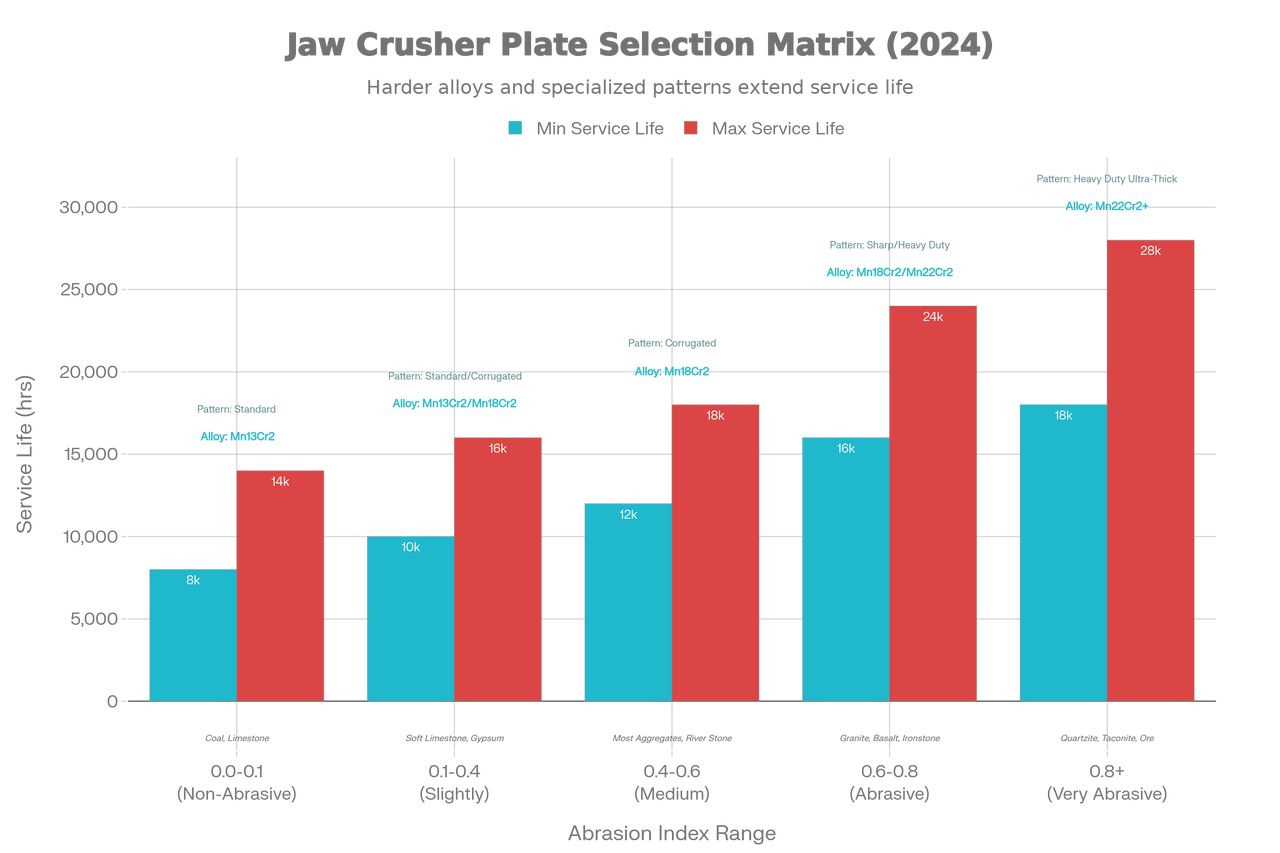
Jaw Crusher Plate Selection Matrix: Matching Abrasion Index to Alloy, Tooth Pattern, and Service Life
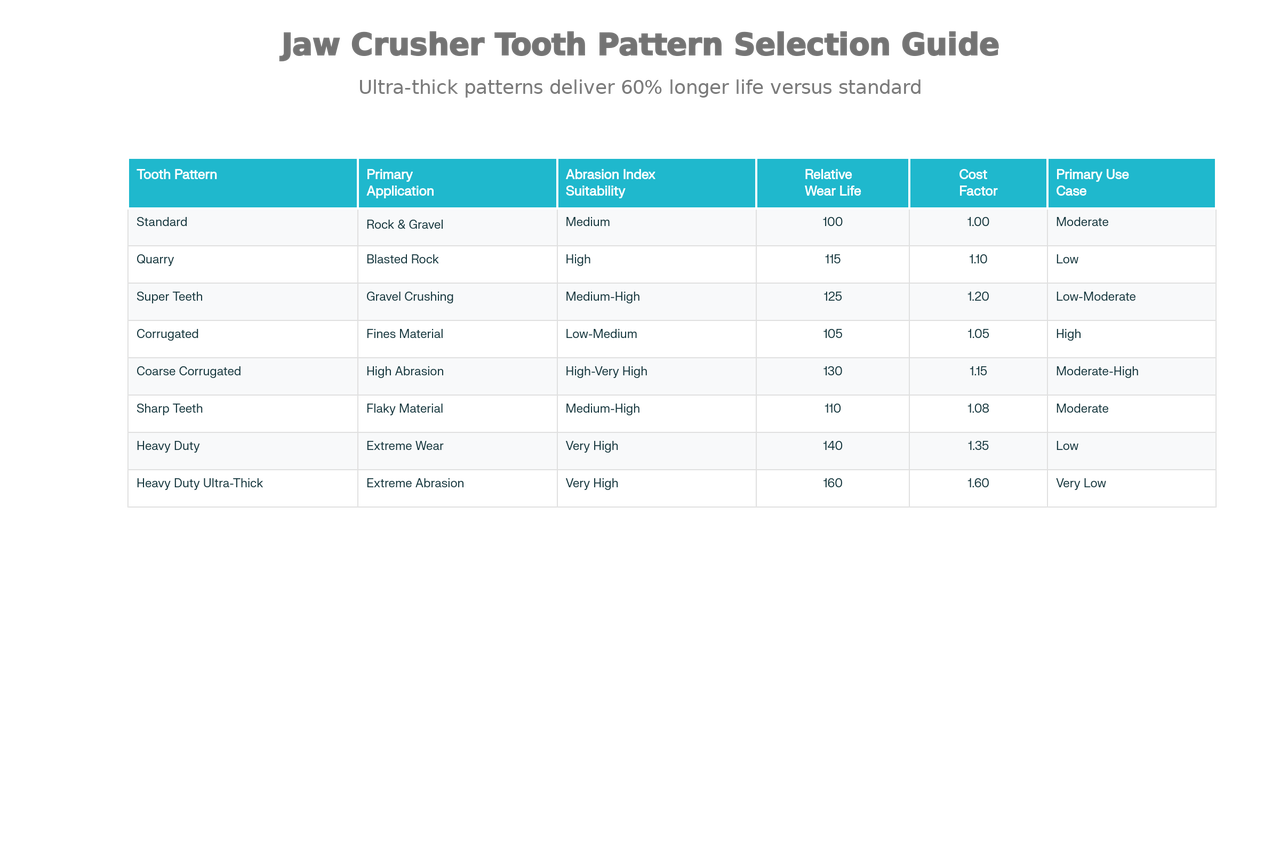
Jaw plate tooth patterns directly influence material grip, fines generation, crushing efficiency, and wear distribution. Selecting the wrong profile causes slabby products (flat fragments unsuitable for concrete), excessive fines dust, or rapid tooth wear.
Design characteristics: Balanced tooth height with moderate spacing
Best for: General rock and gravel crushing applications
Performance profile: Wear life, power requirements, and crushing stresses in good balance
Advantages: Excellent fines removal, reduced slabby product generation, typical factory installation
Industry adoption: Most common profile for mid-sized operations
Caution: Lower performance with heavily abrasive materials
Design characteristics: Flat tooth profile, maximized surface area
Best for: Blasted rock quarries, abrasive materials
Performance profile: Extended lifetime with more wearable manganese steel
Advantages: Flat profile distributes crushing force across larger area, reducing point stress concentrations
Disadvantages: Higher power requirements, increased stress on crusher frame, less favorable for fines removal
Industry adoption: Preferred by large-scale quarry operators processing granite, granite-gneiss
Design characteristics: Larger mass, specially engineered tooth geometry
Best for: Gravel crushing, general applications requiring long wear life
Performance profile: Extended lifetime through enhanced mass and special design
Advantages: Material flows efficiently through large grooves without wearing tooth edges, balanced fines removal
Ideal for: Recycling facilities processing aggregate materials
Limitation: Not suitable for extremely hard rock applications
Design characteristics: Grooved surface with shallow corrugation pattern
Best for: Materials with fine content, small Closed Side Setting (CSS) requirements
Performance profile: Good wear resistance, excellent top-size control
Advantages: Fines flow smoothly through grooves preventing compaction and packing
Use case: Secondary crushing where uniform particle sizing matters
Limitation: Reduced lifetime in highly abrasive applications
Design characteristics: Deeper groove patterns with aggressive corrugation
Best for: Highly abrasive feed materials, large CSS settings
Performance profile: Optimized for maximum abrasion resistance
Advantages: Deep grooves prevent material bridging, material flows freely despite fines
Industry adoption: Mandatory for recycling operations processing concrete/asphalt
Performance metrics: Can increase lifespan by 20–30% versus standard teeth in high-AI applications
Design characteristics: Aggressive pointed geometry for enhanced grip
Best for: Flaky, angular, or smooth feed materials prone to slipping
Performance profile: Superior gripping ability with excellent top-size control
Advantages: Aggressive contact prevents material rotation and sliding
Use case: Recycling facilities processing flat materials (concrete slabs, asphalt chunks)
Caution: Only suitable when AI is moderate; not recommended for extreme abrasion
Design characteristics: Thicker, reinforced tooth structure with increased height
Best for: Extremely abrasive materials, long-term durability requirements
Performance profile: Maximized wear life through enhanced mass and structural strength
Advantages: 30% thicker design extends replacement intervals significantly
Industry adoption: Preferred for continuous high-volume operations in remote locations
Lifetime expectation: 40–50% longer than standard teeth
Design characteristics: Fixed jaw plate with 30mm additional thickness
Best for: Very abrasive materials when combined with CC moving plate
Performance profile: Exceptional wear life in extreme conditions
Special feature: Reserved exclusively for fixed jaw plates to maximize lower-jaw durability
Industry adoption: Premium specification for Sandvik CJ815 and similar large crushers
Cost-benefit analysis: Premium pricing offset by 12+ month extension of replacement intervals
Monolithic construction combining upper and lower plate sections
Can be rotated 180° to extend useful life
Simpler design with fewer replacement components required
Lower manufacturing complexity (more cost-effective to produce)
Easier bolt assembly with fewer fastening points
Faster jaw plate replacement—critical for mobile crusher operations with limited space
Eliminates requirement for center wedges and secondary support components
Straightforward installation process suitable for limited-access maintenance areas
Ideal for smaller to mid-sized crushers with balanced wear patterns
Lower inventory requirements (one plate type vs. multiple sections)
Optimal for materials with uniform abrasion characteristics
Best for operations crushing 8,000–12,000 hours annually
Suitable when wear patterns remain symmetric throughout operational life
Performance rotation strategy: Rotate 180° when lower third exhibits 30% wear
15–25% lower manufacturing cost vs. two-piece equivalent
Reduced inventory carrying costs
Lower replacement parts investment
Ideal for budget-conscious cheap jaw crusher plate manufacturers targeting cost-sensitive operations
Cannot independently replace worn upper vs. lower sections
Less optimal for extreme high-tonnage operations
May require replacement before full theoretical service life exhaustion
Not recommended for highly asymmetric wear environments
Modular construction with independent upper and lower sections
Each section bolts separately to crusher jaw structure
More complex manufacturing requiring precision alignment
Higher manufacturing cost but superior operational flexibility
Each worn section replaces independently (30–40% cost reduction per replacement cycle)
Worn upper section repositions downward where maximum abrasion occurs
Fresh plates install at upper crushing chamber where wear rates lower
Implements strategic rotation extending theoretical service life 40–50%
Ideal for large-capacity operations with high-tonnage throughput
Optimized for high-volume operations (15,000+ annual operating hours)
Accommodates asymmetric wear patterns common in large crushers
Extends overall plate lifetime through strategic component reuse
Rotation strategy: Lower section >50% worn → swap top and bottom dies
20–30% higher initial purchase price
30–50% reduction in cost-per-replacement cycle through section reuse
Lower total cost of ownership for high-throughput operations (3+ years)
Reduced manganese steel consumption (environmental sustainability benefit)
Standard for crushers exceeding 500 ton/hour capacity
Mandatory for mining operations processing taconite or ultra-abrasive ores
Preferred by large aggregate producers targeting cost optimization
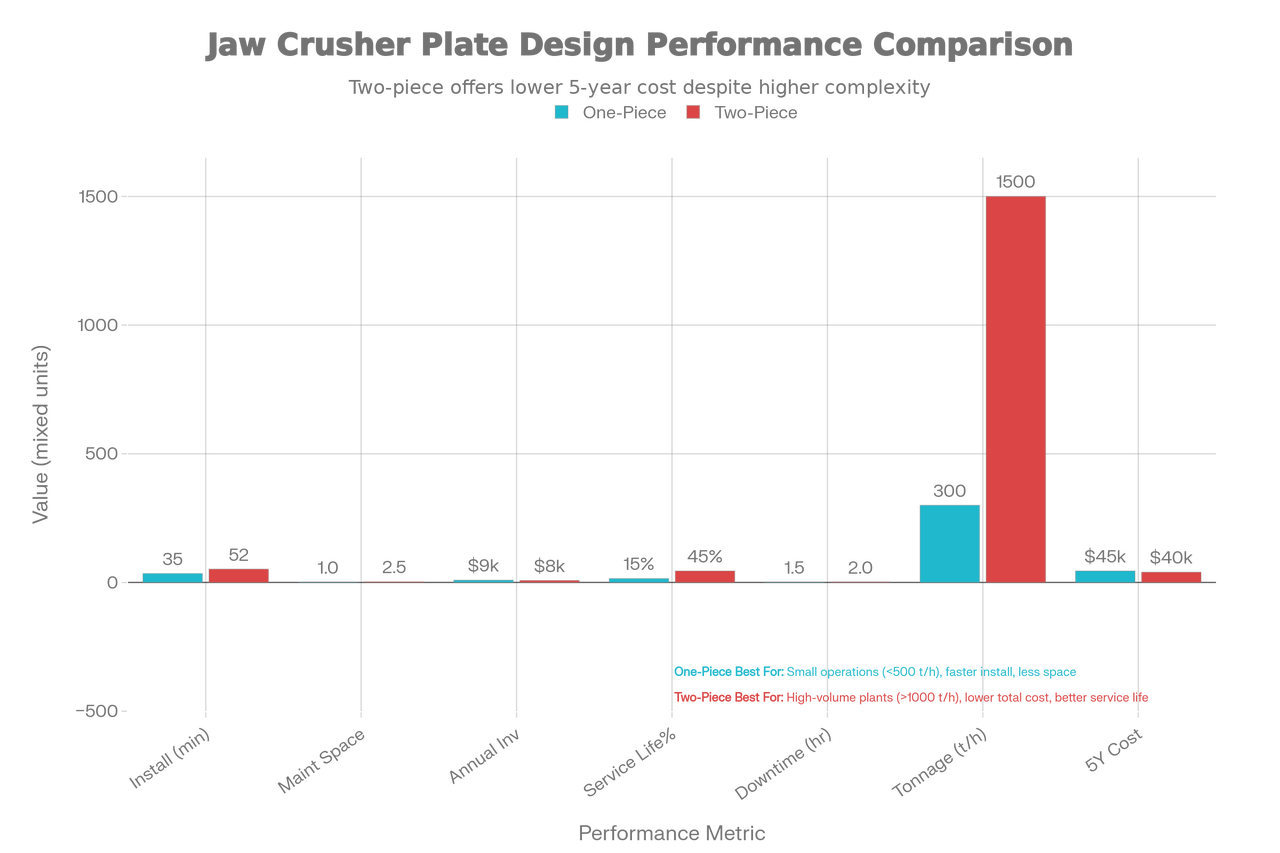
| Evaluation Criteria | One-Piece Design | Two-Piece Design |
| Installation Speed | 30–40 minutes | 45–60 minutes |
| Maintenance Space Requirements | Minimal (mobile-friendly) | Standard to large |
| Replacement Cost (per event) | $4,500–$8,000 | $3,500–$6,500 |
| Service Life Extension Potential | 0–20% (through rotation) | 40–50% (through strategic reuse) |
| Downtime per Replacement | 1–2 hours | 1.5–2.5 hours |
| Optimal Application Tonnage | <500 ton/hour | >500 ton/hour |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Low | High |
| Inventory Management | Simple | Complex (multiple SKUs) |
Offers seven distinct tooth patterns with up to three alloy options (M1, M2, M8)
Fixed plate-moving plate combinations engineered for specific models
CJ815 (JM1513) recommendation: Heavy Duty Ultra-Thick (UT) fixed + Coarse Corrugated (CC) moving
Alloy selection: M9 for extended wear life in high-tonnage quarries
Dimension precision required: ±2mm tolerance mandatory
Complex tooth pattern library with model-specific compatibility
Pre-engineered plate sets for different product gradation requirements
Requires verification against crusher serial number for optimal fit
Cheek plates and deflector components integrate with jaw plate assemblies
Offers toggle-dependent designs where jaw plate selection drives overall crusher geometry
Three-piece toggle construction requires coordinated plate specification
Custom designs available for retrofit applications
Jaw plates labeled "universal" typically fit crushers following standard design patterns
Even minor differences in hole placement or alloy composition affect installation
Dimension verification against machine specifications remains essential
True compatibility assessed case-by-case despite "universal" marketing claims
Before ordering from any cheap jaw crusher plate manufacturer, confirm:
Verify exact model designation (e.g., Sandvik CJ815 vs. CJ412)
Confirm manufacturing year (alloy specifications evolved over decades)
Document serial number for traceability
Jaw opening width (defines maximum jaw plate width)
Plate height and thickness specifications
Bolt hole pattern and spacing (±2mm tolerance critical)
Wedge system type (if applicable)
Current alloy composition (Mn13, Mn18, Mn22)
Historical alloy preference for your specific feed material
ISO certification and quality standards documentation
Feed material type and abrasion index
Current tonnage throughput
Closed side setting (CSS) range
Annual operating hours projection
Request dimensional drawings with tolerance specifications
Confirm 100% inspection verification before shipment
Verify fit guarantee or replacement policy
Document customer references with identical crusher models
Alloy: Mn13Cr2
Tooth Pattern: Standard teeth or wide tooth
Design: One-piece (cost-efficient, straightforward replacement)
Fixed/Moving: Standard specifications sufficient
Rationale: Limestone crushing represents the lowest-stress application. Lower manganese content reduces manufacturing cost while delivering adequate wear resistance. Standard tooth geometry prevents fines compaction in the high-fines-content feed characteristic of limestone operations.
Service life: 10,000–14,000 operating hours
Replacement frequency: Every 12–18 months (typical throughput)
Annual jaw plate investment: $6,000–$12,000
Alloy: Mn18Cr2 (standard) or Mn22Cr2 (premium specification)
Tooth Pattern: Sharp teeth or heavy-duty pattern
Design: Two-piece (maximize service life extension through rotation)
Fixed/Moving: Heavy-duty ultra-thick fixed + coarse corrugated moving
Rationale: Granite and basalt crushing demands premium material specifications and strategic design. Work-hardening manganese content (18–22%) resists particle embedding common in abrasive rock. Two-piece architecture enables strategic rotation extending plate lifetime 40–50%.
Service life: 16,000–24,000 operating hours (two-piece rotation strategy)
Replacement frequency: Every 18–24 months
Annual jaw plate investment: $18,000–$28,000
ROI: Premium pricing offset by 50% extension in operational periods
Alloy: Mn22Cr2 (abrasion-resistant specification)
Tooth Pattern: Coarse corrugated or anti-slab design
Design: Two-piece (essential for high-throughput continuous operations)
Fixed/Moving: Heavy-duty ultra-thick fixed + sharp or aggressive moving
Rationale: Recycled concrete and asphalt represent extreme-abrasion applications combining hard embedded aggregates with embedded rebar/steel reinforcement. Aggressive tooth patterns (coarse corrugated, sharp) maintain material grip despite slick surfaces and irregular shapes. Ultra-thick configurations tolerate extreme wear rates.
Service life: 14,000–20,000 operating hours
Replacement frequency: Every 12–16 months (continuous operation model)
Annual jaw plate investment: $24,000–$35,000+
Downtime reduction: Strategic two-piece rotation minimizes crusher idle time
Alloy: Mn22Cr2 with advanced chromium enhancement
Tooth Pattern: Heavy-duty ultra-thick (UT) fixed only
Design: Two-piece (mandatory for 24/7 continuous mining operations)
Fixed/Moving: Ultra-thick fixed (30mm additional thickness) + coarse corrugated moving
Performance Expectations:
Service life: 18,000–28,000+ operating hours (through strategic rotation)
Replacement frequency: Every 24–36 months (extended interval critical for remote mining)
Annual jaw plate investment: $32,000–$48,000
Strategic value: Extended intervals minimize mining operation disruption
Visually inspect jaw plate surfaces for visible cracking or spalling
Verify all bolts remain tight (vibration gradually loosens fasteners)
Check for material bridging or packing within crushing chamber
Clean debris accumulation from tooth grooves
Measure jaw plate wear depth at three locations (upper, middle, lower)
Document wear progression rate (millimeters per operating hour)
Inspect bolt heads and threads for corrosion or degradation
Lubricate toggle joint assemblies per manufacturer specifications
Calculate projected service life based on observed wear rates
Procure replacement plates in advance (lead time planning)
Schedule rotation or replacement during planned maintenance windows
Adjust crusher operating parameters if wear accelerates unexpectedly
Remove jaw plates and inspect internal jaw structure for cracks
Clean all mounting surfaces to manufacturer specifications
Verify jaw alignment within tolerance parameters
Document all maintenance activities for equipment history records
Fixed jaw plate: Rotate 180° when lower third exhibits 30% wear
Moving jaw plate: Rotate when asymmetric center wear becomes noticeable
Timing frequency: Typically every 4–8 months depending on material and tonnage
Lower section rotation trigger: >50% worn lower section
Strategic repositioning: Move work-hardened upper plate downward where maximum abrasion occurs
Install new/less-worn plates at upper chamber (lower stress environment)
Rotation frequency: Every 6–12 months depending on application intensity
Shut down crusher and verify electrical system de-energization
Allow cooling period (2–4 hours for heat dissipation)
Remove safety guards and access covers
Loosen and remove mounting bolts (cap nuts simplify removal process)
Support jaw plates with hydraulic jacks to prevent unexpected dropping
Document wear pattern photography for wear analysis
Rotate or reposition plates according to strategy
Install bolts hand-tight first, then torque to specification
Test crusher briefly before resuming full production
One-piece plate lifecycle: 1 full replacement per ~12 months = $6,000–$12,000 annually
Two-piece plate with rotation strategy: 1 lower replacement + reposition upper = $3,500–$7,000 every 6–12 months, net 30–50% savings
ISO 9001:2008 quality management certification (mandatory minimum)
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) compliance documentation
ISO 14001 environmental management certification
ISO 45001 occupational health and safety certification
ASTM or equivalent material testing standards
Advanced casting technology (3D sand printing reduces development cycles to 2 weeks)
Complete process automation from raw material through final inspection
100% final inspection coverage rate before shipment
In-house alloy composition laboratory for quality verification
Heat treatment capability (quenching, tempering for hardness optimization)
Professional technical team (minimum 12 engineers recommended)
Documented collaboration with university research institutions
Active participation in national casting standards development
Demonstrated innovation in specialized alloy formulations
Custom design capability for non-standard crusher models
Minimum 80,000 tons annual production capacity (ensures supply security)
Average delivery cycle < 14 days (logistics efficiency)
Flexibility to accommodate rush orders
Global logistics network for international shipment
Consistent on-time delivery documentation (>95% target)
24/7 technical support availability
Responsive engineering team for application consultation
Detailed technical documentation in multiple languages
Customer training programs on proper installation/maintenance
Warranty coverage specifics and replacement policies
Established relationships with major industry customers
Recommended: Mid-tier Chinese manufacturers emphasizing cost efficiency
Focus: Mn13Cr2, one-piece designs, standard tooth patterns
Advantage: 30–40% cost reduction vs. premium suppliers
Consideration: Verify dimensional accuracy through 100% inspection guarantee
Recommended: Established regional suppliers with proven track records
Focus: Mn18Cr2, balanced quality/cost positioning
Advantage: Local technical support, faster delivery, reasonable pricing
Consideration: Request customer references from similar-tonnage operations
Recommended: Premium suppliers with mining-specific certifications
Focus: Mn22Cr2, custom designs, two-piece configurations
Advantage: Dedicated account management, customized solutions, strategic partnership
Consideration: Long-term volume agreements reduce per-unit costs
35,000 square meter facility with 98.36-acre complex
80,000 tons annual production capacity
236 employees with specialized technical expertise
ISO 9001 certification with 100% final inspection coverage
13 invention patents + 45 utility model patents (documented innovation)
DISA vertical casting lines with advanced automation
3D sand mold printing (2-week product development cycles)
Complete quality control: raw material through shipment
Comprehensive mining machinery wear parts including jaw crusher plates
Concrete plant components
Metallurgical industry products
Asphalt machinery components
Automated intelligent production systems (ERP, MES, OA, CRM integration)
Professional inspection and final quality control personnel
100% final inspection coverage rate
Traceability documentation for batch accountability
"National Outstanding Intelligent Manufacturing Scenario" award
"Anhui Province Intelligent Factory" designation
"Specialized new 'little giant'" recognition
"National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise" certification
This profile demonstrates the characteristics distinguishing premium cheap jaw crusher plate manufacturers: documented quality systems, production capacity, technical expertise, and measurable industry recognition—not merely price positioning.
Consult geological surveys or material testing labs for Abrasion Index determination
Cross-reference material type against industry classification tables
Account for seasonal variations (moisture content affects abrasiveness)
Project annual tonnage throughput
Verify exact crusher model, serial number, and manufacturing year
Obtain manufacturer technical drawings with tolerance specifications
Confirm mounting system (bolt-on vs. wedge-style)
Document current jaw plate specifications if replacing existing plates
Select appropriate alloy (Mn13, Mn18, Mn22) based on abrasion index
Choose tooth pattern optimized for feed material characteristics
Determine design architecture (one-piece vs. two-piece) based on tonnage
Project replacement frequency and inventory planning
Verify quality certifications and standards compliance
Request dimensional verification guarantee
Collect customer references processing identical materials
Compare pricing across 3–5 qualified suppliers
Evaluate technical support availability and responsiveness
Calculate cost per ton of material processed
Project service life extension from premium vs. budget specifications
Evaluate downtime costs associated with replacement frequency
Assess impact on product quality and market value
Consider environmental sustainability factors (manganese consumption)
Selecting a cheap jaw crusher plate manufacturer represents a critical operational decision extending far beyond simple price shopping. The optimal choice balances:
Technical compatibility with your specific crusher model
Material specification aligned to feed material abrasion characteristics
Design configuration matching operational throughput and flexibility requirements
Supplier reliability ensuring quality assurance and technical support
Total cost of ownership incorporating service life, downtime, and productivity impacts
By implementing the systematic evaluation framework presented throughout this guide—from abrasion index classification through supplier qualification—you'll move beyond bottom-line pricing toward strategic sourcing that delivers measurable operational value, extended equipment lifespan, and superior profitability.
The decision to invest premium specifications or pursue budget efficiency ultimately reflects your operational priorities: continuous maximum-capacity production favors premium two-piece configurations and Mn22Cr2 alloys; periodic or seasonal operations permit one-piece designs with standard Mn13–Mn18 compositions. Neither approach is inherently superior—but the intentional selection methodology matters absolutely.