Selecting the right continuous concrete batching plant is one of the most critical decisions for construction companies, precast manufacturers, and concrete producers. This comprehensive technical guide addresses the needs of procurement teams, engineers, and project managers who are evaluating equipment options to meet their specific operational requirements. With production capacity ranging from 8 m³/hour for mini batch plants to over 200 m³/hour for large stationary installations, understanding the technical specifications and selection criteria is essential for making informed decisions that will impact your project's efficiency, quality, and profitability.
The equipment selection process extends far beyond capacity considerations. It encompasses mixer types, automation capabilities, cement storage solutions, aggregate batching systems, control technology, manufacturer reliability, and comprehensive after-sales support. This guide provides detailed technical insights to help you navigate through these critical factors and select a continuous concrete batching plant that aligns perfectly with your operational needs.
The foundation of any equipment selection process begins with a clear understanding of your production requirements. Production capacity directly influences the size, cost, and operational scope of your continuous concrete batching plant installation.
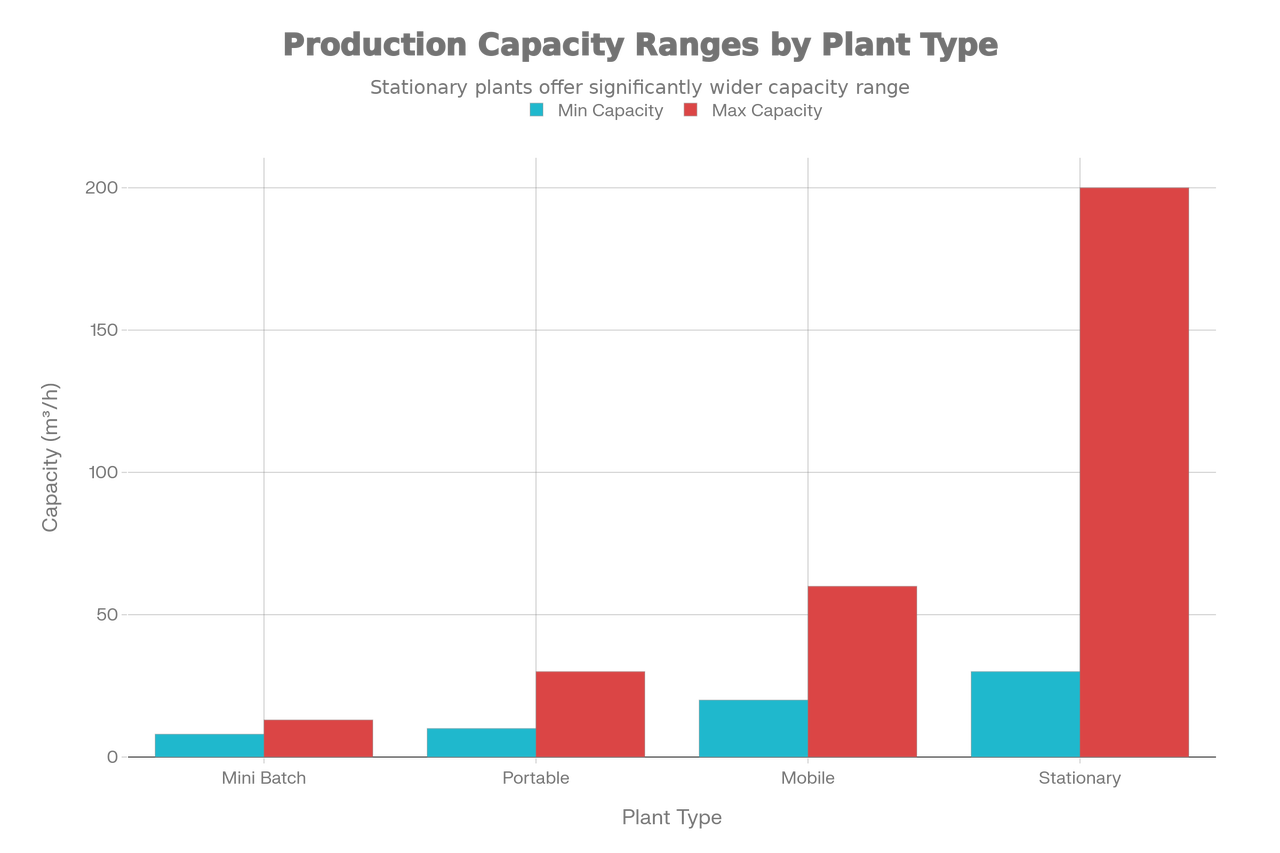
Mini Batch Plants produce between 8-13 m³/hour, making them ideal for small residential projects, repair work, and situations where space constraints limit equipment size. These compact installations require minimal foundation preparation and can be set up quickly on site.
Portable Concrete Plants deliver 10-30 m³/hour output, suitable for medium-scale projects with moderate concrete demands. Their compact design and integrated components allow for relatively quick relocation between job sites while maintaining good production efficiency.
Mobile Concrete Plants operate in the 20-60 m³/hour capacity range and are designed for temporary installations requiring frequent site-to-site relocation. These units come pre-wired and pre-assembled, significantly reducing installation time compared to stationary systems.
Stationary Concrete Plants represent the largest category with production capacities ranging from 30 to 200 m³/hour or higher. These permanent installations are engineered for large-scale, long-term projects requiring consistent, high-volume concrete production.
When determining your capacity requirements, consider these critical factors:
Daily concrete consumption based on project schedule and construction methodology
Peak demand periods and average production requirements
Future expansion potential and anticipated project growth
Supply frequency needs and on-site storage limitations
Multiple site operations and whether equipment relocation is necessary
Many contractors underestimate capacity needs initially, resulting in production bottlenecks. Conversely, oversized installations lead to unnecessary capital expenditure and operational inefficiency. The optimal selection requires balancing current project demands with realistic growth projections.
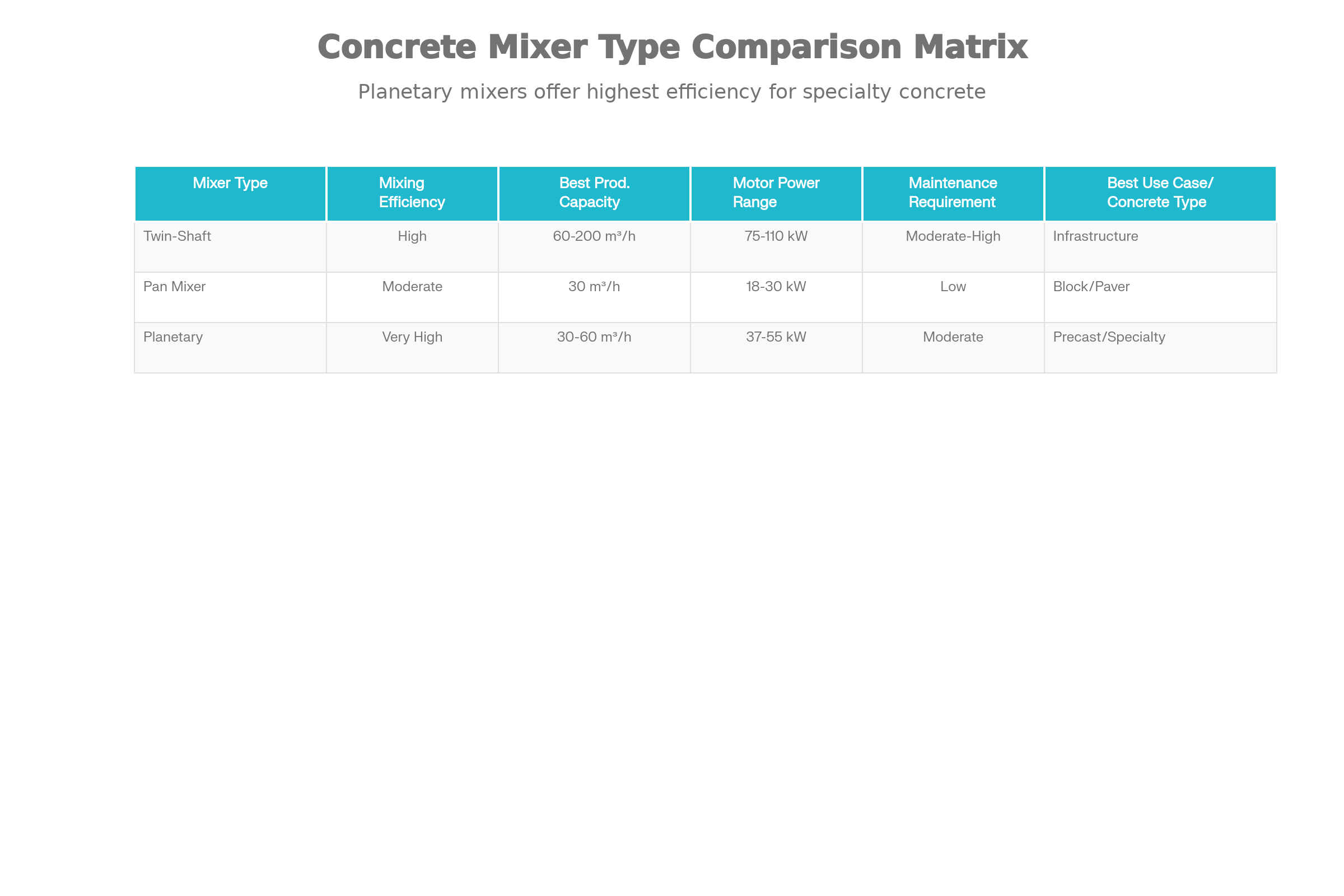
Technical Specifications of Twin-Shaft Mixers:
| Capacity | Internal Volume | Wet Concrete Output | Motor Power | Wear Plate Thickness |
| 60 m³/h | 1500 L | 1000 L | 2 × 18.5 kW | 25mm base, 15mm side |
| 90 m³/h | 1500 L | 1500 L | 2 × 22 kW | 25mm base, 15mm side |
| 120 m³/h | 2250 L | 2000 L | 2 × 37 kW | 30mm base, 20mm side |
| 180 m³/h | 3000 L | 3000 L | 2 × 45 kW | 30mm base, 20mm side |
Key Advantages:
Superior mixing efficiency with synchronized dual-shaft mechanism delivering uniform concrete distribution
Fast mixing cycles typically 60-72 seconds, maximizing production throughput
Heavy-duty construction with wear-resistant Ni-Hard cast components ensuring extended service life
Automatic lubrication systems with programmable digital displays reducing maintenance interventions
Multiple motor capacity options optimizing power consumption for different production scales
Replaceable wear components that extend mixer longevity while maintaining concrete quality
The twin-shaft design excels at mixing large aggregate sizes up to 80-100mm, making it ideal for infrastructure projects, dam construction, and mass concrete applications. The synchronized shafts prevent material segregation and ensure consistent concrete strength across all batches.
Pan mixers utilize a rotating pan base with fixed mixing arms, providing a different mixing mechanism particularly suited for precast concrete, block manufacturing, and paving applications. These mixers are known for their compact footprint and efficient mixing action suitable for lower to medium production volumes.
| Capacity | Internal Volume | Wet Concrete Output | Motor Power | Aggregate Size | Best Applications |
| 30 m³/h | 750 L | 500 L | 22 kW | 80/60mm | Precast, Blocks |
Pan mixers feature a robust six-arm mixing system that ensures even aggregate distribution throughout the concrete mass. The adjustable discharge gates provide controlled concrete flow, preventing spillage and material loss during transfer. Heavy-duty wear plates constructed from 15mm Hardox base material with 10mm sides withstand continuous operation in demanding production environments.
The pan mixer's design proves particularly effective for producing colored concrete, specialty finishes, and precast elements where precise control over mixing time and consistency is paramount. The compact design makes these units suitable for precast plants operating in space-constrained environments.
Technical Specifications of Planetary Mixers:
| Capacity | Internal Volume | Wet Concrete Output | Motor Power | Reducer | Best For |
| 30 m³/h | 750 L | 500 L | 18.5 kW | Brevini Planetary | Precast Elements |
| 60 m³/h | 1500 L | 1000 L | 45 kW | Brevini Planetary | UHPC, Specialty |
Planetary mixers employ multiple mixing tools including three mixing feet and one scraper blade, optimizing performance across different mix designs and aggregate sizes. These units are equipped with high-performance Brevini planetary reducers, ensuring smooth operation and minimal maintenance requirements. The wear-resistant Ni-Hard cast components maintain their precision over extended operational periods.
Proper capacity selection requires detailed analysis of concrete consumption patterns and project timelines. Consider the following framework:
Recommended Plant Capacity: 30-60 m³/hour
Typical Installation: Mobile or Portable Systems
Project Duration: 3-12 months
Suitable for: Commercial buildings, residential complexes, small infrastructure
Large Infrastructure Projects (Daily Consumption 500-1,000+ m³)
Recommended Plant Capacity: 90-180 m³/hour
Typical Installation: Stationary Systems
Project Duration: 12+ months
Suitable for: Major highways, dams, bridges, substantial precast operations
The relationship between daily consumption and plant capacity should incorporate production efficiency factors including mixing cycles, material handling time, and quality control intervals. A plant operating at 90% capacity typically delivers optimal performance, while sustained operation above 95% capacity risks equipment stress and maintenance complications.
Cycle Time Calculations:
Continuous concrete batching plants operate on defined cycle times—the duration required to batch, mix, and discharge one concrete load. Standard cycle times for properly maintained equipment range from 60-75 seconds. This means a 60 m³/h plant theoretically completes approximately 60 batches per hour (3,600 seconds ÷ 60-second cycle time = 60 batches).
Practical production typically achieves 85-90% of theoretical capacity due to quality control procedures, material changeovers, and scheduled maintenance. Therefore, when planning procurement for a 60 m³/h requirement, selecting equipment rated for 70 m³/h provides the necessary operational headroom.
Standard Aggregate Batching System Specifications:
| Model | Weighing Hopper Volume | Storage Capacity | Production Capacity | Weighing Accuracy | Max Weight | Aggregate Categories |
| AG800 | 0.8 m³ | 2×2 m³ | 48 m³/h | ±2% | 1,500 kg | 2 types |
| AG1200-3 | 1.2 m³ | 4×2.2 m³ | 60 m³/h | ±2% | 2,000 kg | 4 types |
| AG1600-2 | 1.6 m³ | 4×3.7 m³ | 80 m³/h | ±2% | 3,000 kg | 4 types |
| AG2400 | 2.4 m³ | 3×12 m³ | 120 m³/h | ±2% | 4,000 kg | 3 types |
| AG3200 | 3.2 m³ | 3×20 m³ | 160 m³/h | ±2% | 5,000 kg | 3 types |
Aggregate batching systems feature multiple hoppers that store different aggregate types (fine sand, coarse aggregates, specialty materials) separately. High-precision load cell sensors mounted beneath each hopper bin continuously monitor material weight, feeding this data to the control system for real-time adjustment. The system employs pneumatic door gates or belt conveyors for controlled material discharge, ensuring accurate portioning within acceptable tolerances.
The number of aggregate categories your plant can handle influences the versatility of concrete mix designs. Plants handling 3-4 aggregate types provide flexibility for standard concrete mixes, while systems managing 5-6+ types accommodate specialized applications including colored concrete, decorative finishes, and high-performance mixes.
Cement storage represents a critical infrastructure component for uninterrupted concrete production. Modern cement silos provide sealed storage preventing moisture ingress and dust contamination while enabling efficient material conveyance to the mixing system.
| Silo Capacity | Diameter | Number of Layers | Wall Thickness | Leg Distance | Volume (M³) |
| 50T | 3,200mm | 3 | 3-5mm | 2,108mm | 40.77 |
| 100T | 3,200mm | 6 | 3-4-5mm | 2,108mm | 78.46 |
| 150T | 3,800mm | 6 | 3-4-5mm | 2,547mm | 113.08 |
| 200T | 4,500mm | 6 | 3-4-5-6mm | 3,001mm | 160 |
| 300T | 5,000mm | 7 | 4-5-6mm | 3,208mm | 220 |
| 400T | 5,700mm | 7 | 4-5-6-8mm | 2,670mm | 300.77 |
Silo Selection Criteria:
Production Continuity: Calculate silo capacity based on daily cement consumption and restock frequency. A 200T silo supporting a 60 m³/h plant (consuming approximately 300-350 kg/m³) provides 2-3 days of continuous operation
Supply Schedule: Coordinate silo capacity with cement delivery frequency; align capacity with supplier schedules and transportation constraints
Space Requirements: Larger silos require proportionally greater footprint; assess available site space including clearance for truck access and material delivery
Maintenance Access: Ensure adequate space around silos for internal cleaning, valve maintenance, and equipment servicing
Modern cement silos incorporate intelligent material-level sensing systems detecting cement height through electronic sensors, triggering refill alerts when inventory reaches predetermined thresholds. This automation prevents production interruptions due to cement depletion while optimizing inventory management.
Dust collection systems installed at silo tops capture airborne cement particles during loading operations, reducing environmental emissions and material losses. These systems employ vibrating mechanisms that automatically clear accumulated dust, maintaining system efficiency throughout extended operational periods.
Modern continuous concrete batching plants leverage advanced automation technology through Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) systems integrated with Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) platforms. These systems function complementarily—the PLC executes precise control logic for batching, mixing, and transfer operations, while the SCADA system provides visual monitoring interfaces and operator controls.
Key Automation System Capabilities:
Continuous sensor data collection from aggregate weighing systems, mixer load cells, cement conveyors, and water distribution systems
Real-time adjustment of operation parameters maintaining target concrete specifications
Simultaneous operation of multiple equipment systems with coordinated sequencing
Automatic safety interlocks preventing equipment operation when conditions fall outside safe parameters
Data Logging and Performance Reporting
Comprehensive production records documenting each concrete batch, ingredients, mixing times, and quality parameters
Historical data analysis identifying production trends, equipment performance, and efficiency metrics
Official receipt generation for customer documentation and quality assurance
Predictive maintenance alerts based on equipment operating hours and performance trends
Remote Accessibility and Troubleshooting
Remote monitoring capability enabling operators and technical support staff to observe plant operation from mobile devices or external locations
Diagnostic data transmission facilitating rapid troubleshooting with manufacturer support teams
Over-the-air software updates implementing system improvements and feature enhancements
Reduced downtime through expedited problem identification and resolution
Energy Optimization
Smart power management systems continuously monitoring energy consumption across all plant components
Automated motor speed adjustments reducing unnecessary power draw during partial-load operations
Scheduled maintenance alerts preventing equipment inefficiency due to component wear or system degradation
Energy efficiency reporting supporting operational cost reduction initiatives
Safety Integration
Automated safety protocols limiting direct human involvement in hazardous operations
Emergency stop mechanisms functioning independently from primary control systems
Personnel proximity detection preventing equipment operation in occupied areas
Compliance documentation supporting workplace safety certifications
The choice between mobile and stationary continuous concrete batching plant configurations significantly impacts project flexibility, operational costs, and production capabilities. This comparison examines critical decision factors across multiple operational dimensions.
Installation Time and Site Preparation:
Stationary Concrete Plants typically require 2-4 weeks for comprehensive installation including site preparation, foundation construction, equipment assembly, and system integration. The larger installation footprint and interconnected component systems necessitate careful coordination and extended commissioning procedures. However, the permanent installation provides superior stability and operational reliability for long-duration projects.
Mobility and Operational Flexibility:
Mobile plants excel when project requirements necessitate site relocation, whether due to multiple construction locations or temporary project status. The integrated design reduces disassembly time to 2-3 days, enabling rapid transitions between job sites. This flexibility supports contract production operations serving multiple customers across geographically dispersed locations.
Stationary plants remain fixed at single locations, providing strategic advantages for centralized production supporting large infrastructure projects, precast facilities, or long-term supply contracts. Once established, stationary systems deliver consistent production without relocation disruptions.
Mobile concrete batching plants typically deliver capacities between 20-60 m³/hour, optimized for temporary installations and projects requiring moderate to substantial concrete volumes. While highly efficient, mobile units sacrifice raw capacity for portability.
Stationary systems accommodate production capacities from 30 to 200+ m³/hour, enabling high-volume production operations supporting major infrastructure and precast manufacturing. The larger capacity enables serving multiple concurrent projects from single installations.
| Operational Factor | Mobile Plants | Stationary Plants |
| Installation Time | 3-5 days | 2-4 weeks |
| Setup Space Required | Minimal (flat surface) | Substantial (foundation/utilities) |
| Foundation Requirements | None/minimal | Substantial (concrete pads) |
| Production Capacity Range | 20-60 m³/h | 30-200+ m³/h |
| Relocation Time | 2-3 days | Not relocatable |
| Flexibility for Multiple Sites | Excellent | Limited |
| Long-term Project Economics | Higher cost/m³ | Lower cost/m³ |
| Quality Consistency | High | High |
| Maintenance Access | Good | Excellent |
| Capital Investment | Lower initial | Higher initial |
| Operational Lifespan | 8-12 years | 15-20+ years |
Wear Component Material Specifications:
Ni-Hard Cast Material: Superior hardness resisting aggregate abrasion throughout extended service periods; provides 2-3x longevity compared to standard steel
Thickness Specifications: 25-30mm base plates with 15-20mm side plates accommodating aggressive mixing action
Replacement Indicators: Color-coding or measurement systems tracking wear progression, alerting operators when replacement becomes necessary
Aggregate Hopper Liners
Hardened Steel Construction: Resists impact and abrasion from continuous aggregate discharge
Replacement Frequency: Typically 18-24 months depending on material type and production intensity
Conveyor Belts and Pulleys
Industrial-Grade Materials: Constructed from reinforced rubber with embedded steel cables ensuring durability and load-bearing capacity
Tension Monitoring: Automatic adjustment systems maintaining optimal belt tension throughout operational periods
Cement Silo Components
Corrosion-Resistant Coatings: Protect metallic surfaces from moisture and chemical deterioration
Sealed Connections: Prevent moisture ingress that would compromise cement quality
Procuring equipment from manufacturers emphasizing wear-resistant component selection reduces long-term operating costs through extended component life and reduced maintenance interventions.
Weighing System Specifications:
Tolerance Standard: ±2% across all aggregate categories
Load Cell Technology: Multiple load cells beneath each hopper bin providing redundant measurement and sensor failure detection
Calibration Protocol: Monthly calibration against certified standards ensuring sustained accuracy
Real-time Adjustment: Automatic gate positioning based on actual vs. target weights within measurement cycles
Cement Weighing Accuracy
Tolerance Standard: ±1% ensuring precise cement proportioning
Specialized Load Cells: High-sensitivity sensors accommodating cement's lower density compared to aggregates
Dust Consideration: System compensation accounting for dust settlement during measurement cycles
Water Proportioning
Flow Meter Technology: Precision measurement of water addition to achieve target water-cement ratios
Temperature Compensation: Automatic adjustment for temperature effects on water density
Maintaining these accuracy tolerances demands regular maintenance including load cell calibration, software verification, and sensor cleaning. Dust accumulation on load cell sensing surfaces introduces measurement errors; weekly inspection and cleaning of sensor areas prevents accuracy drift.
Selecting the optimal continuous concrete batching plant requires systematic evaluation across technical, operational, financial, and support dimensions. This framework guides engineers and procurement teams through comprehensive assessment:
Production Requirement Analysis
Calculate daily concrete consumption considering project schedule, construction methodology, and peak demand periods
Determine required plant capacity incorporating 10-15% operational headroom
Project timeline influences equipment configuration—short-term projects favor mobile solutions, long-term operations justify stationary investments
Assess future expansion potential and whether current equipment selection accommodates anticipated growth
Technical Specification Validation
Confirm mixer type selection matches concrete type requirements (ready-mix requires twin-shaft efficiency; specialty work may justify planetary accuracy)
Verify cement storage capacity aligns with consumption rates and supply logistics
Validate aggregate batching system accommodates all required concrete mix designs
Assess automation integration requirements and control system complexity
Reliability and Quality Assurance
Review manufacturer quality certifications (ISO standards, CE compliance)
Evaluate equipment durability through warranty terms and expected operational lifespan
Assess wear part quality and component replacement frequency
Consider manufacturer reputation, industry references, and customer satisfaction ratings
Installation and Operational Considerations
Evaluate site space requirements, foundation specifications, and utility connections
Assess installation timeline impacts on project scheduling
Consider equipment accessibility for maintenance and component replacement
Review operator training requirements and support documentation
Financial Analysis
Compare total cost of ownership including capital investment, installation, operational expenses, maintenance, and wear parts
Calculate cost per cubic meter of concrete produced
Model payback period and return on investment
Consider financing options and equipment leasing alternatives
Manufacturer and Support Evaluation
Verify spare parts availability and standard delivery timelines
Confirm technical support accessibility, response times, and service quality
Assess training program comprehensiveness and documentation quality
Review warranty coverage and optional extended service agreements
Evaluate after-sales service network proximity and support capabilities
Equipment selection should extend beyond technical specifications to encompass comprehensive after-sales support ensuring optimal equipment performance throughout its operational lifespan. Established manufacturers prioritize customer support as core business function.
Top manufacturers including ASTEC Industries, Stephens Manufacturing, Vince Hagan Company, MEKA Global, and Semix Global distinguish themselves through comprehensive service networks, spare parts availability, and technical expertise. These organizations operate global service operations with regional support centers enabling rapid response to equipment issues and maintenance requirements.
After-Sales Service Components:
Turnkey plant setup including equipment positioning, utility connections, and system calibration
On-site operator training ensuring personnel proficiency with plant operations and maintenance protocols
Comprehensive system testing validating equipment functionality before production initiation
Continuous Technical Support
24/7 technical support lines connecting operators with experienced technicians for rapid problem-solving
Remote diagnostic capabilities enabling manufacturers to identify issues without on-site visits
Online knowledge bases and documentation resources supporting operator self-troubleshooting
Spare Parts Management
Extensive spare parts inventory ensuring rapid availability of replacement components
Overnight or next-day delivery options for critical components minimizing production downtime
Genuine parts certification guaranteeing compatibility and performance
Planned Maintenance Services
Scheduled preventive maintenance programs extending equipment operational lifespan
Expert lubrication and calibration services optimizing equipment efficiency
Wear component monitoring and proactive replacement recommendations
Extended Service Agreements
Comprehensive maintenance packages covering labor, parts, and routine service
Performance-based agreements guaranteeing uptime percentages and rapid response times
Training program extensions keeping operators current with equipment upgrades and procedural changes
For additional technical resources and information on wear parts and maintenance components, professional suppliers like https://www.htwearparts.com/ provide extensive product catalogs and technical support services.
Regular maintenance schedules directly impact equipment longevity and operational reliability. Organizations should implement systematic maintenance protocols addressing daily, weekly, monthly, and long-term service requirements.
Visual inspection of structural components for wear, cracks, or damage
Safety device verification ensuring emergency stops and guards function correctly
Belt and chain inspection for tension, wear, and proper alignment
Weekly Maintenance Tasks
Fluid level checks for hydraulic systems and cooling circuits
Fastener verification ensuring all bolts and nuts remain secure
Electrical system inspection checking for corrosion and loose connections
Monthly Maintenance Tasks
Detailed wear component assessment identifying components requiring replacement
Bearing lubrication following manufacturer specifications
Structural integrity examination detecting rust or stress damage
Long-Term Maintenance Planning
Major equipment overhauls every 1-2 years involving comprehensive disassembly and component inspection
Detailed maintenance logging tracking all service activities and identifying recurring issues
Spare parts inventory management ensuring critical components remain readily available
While initial capital investment captures attention, comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider total cost of ownership across the equipment's operational lifespan.
Capital Investment: Equipment purchase and delivery
Mini/Portable: $50,000-$150,000
Mobile: $150,000-$400,000
Stationary: $300,000-$1,000,000+
Installation Costs: Foundation, utilities, commissioning
Mobile: $10,000-$30,000
Stationary: $50,000-$200,000+
Annual Operating Expenses:
Fuel/Power: $15,000-$50,000 annually
Maintenance and service: $10,000-$30,000 annually
Operator labor: $60,000-$150,000 annually
Wear parts and replacements: $5,000-$20,000 annually
Financial Justification:
Selecting the optimal continuous concrete batching plant requires systematic evaluation of production requirements, technical specifications, operational flexibility, manufacturer support, and financial considerations. Mobile plants deliver flexibility and rapid deployment, proving cost-effective for temporary projects and multiple-site operations. Stationary plants provide superior production capacity and operational efficiency, justifying their selection for large-scale, long-duration projects.
Regardless of configuration choice, prioritize manufacturers demonstrating commitment to quality, comprehensive after-sales support, and technical expertise. Investments in equipment featuring premium wear components, precise weighing systems, and advanced automation deliver sustained value through extended operational life, reduced maintenance costs, and superior concrete quality.
For detailed technical consultation and custom equipment recommendations tailored to your specific project requirements, professional equipment manufacturers provide expert guidance supporting optimal purchasing decisions. Consulting with experienced technical sales representatives ensures equipment specifications precisely match your operational needs while maximizing long-term return on investment.