Jaw crusher tooth plates represent one of the most critical wear components in aggregate production, mining operations, and recycling facilities. These hardened steel components endure repeated impact forces exceeding several thousand kilonewtons per minute during each compression cycle, translating to 250-400 reciprocal movements per minute depending on operating parameters and material characteristics. For operations processing 200+ tons per hour, unplanned downtime from premature plate failure creates immediate revenue losses ranging from $10,000 to $50,000 per hour of interruption, making strategic maintenance and lifespan extension economically paramount.
The operational reality for most crushing facilities reveals a critical performance gap: equipment operators often achieve only 50-60% of theoretical plate lifespan through reactive maintenance approaches, while those implementing comprehensive preventive strategies routinely extend component life by 30-50% while simultaneously reducing maintenance costs by 25-40%. This comprehensive guide synthesizes evidence-based practices, quantitative wear data, and supplier selection frameworks that equipment operators, maintenance professionals, and procurement teams require to optimize jaw crusher tooth plate performance, minimize downtime, and improve total cost of ownership across diverse crushing applications.
Jaw crusher plates experience multiple simultaneous wear mechanisms that progressively degrade material properties and reduce crushing efficiency. The primary wear modes include chisel cutting wear from repeated impact and extrusion cycles, fatigue wear from cyclic stress accumulation, oxidative corrosion from moisture and atmospheric exposure, and abrasive wear from feed material interaction.
The reciprocal jaw motion creates a complex stress distribution across plate surfaces. In double-toggle jaw crushers, vertical swing displacement significantly exceeds horizontal movement, causing extended material sliding that produces pronounced wear patterns, particularly near the discharge port where compressive forces concentrate. This vertical stress concentration causes 50-70% more wear at the lower plate regions compared to upper sections, establishing asymmetric wear patterns that require strategic rotation protocols to maximize utilization of available material.
Material composition directly determines wear resistance capacity. High-manganese steel (Mn13Cr2) provides cost-effective performance through self-hardening characteristics during impact, developing work-hardened surface layers that resist abrasion. However, standard manganese formulations maintain optimal hardness only within specific temperature and stress ranges. Alloy steel variants with chromium additions (Mn18Cr2, Mn22Cr2) provide superior hardness maintenance across broader operating conditions, while specialized compositions incorporating titanium carbide (TIC) inserts deliver exceptional wear resistance for ultra-abrasive applications.
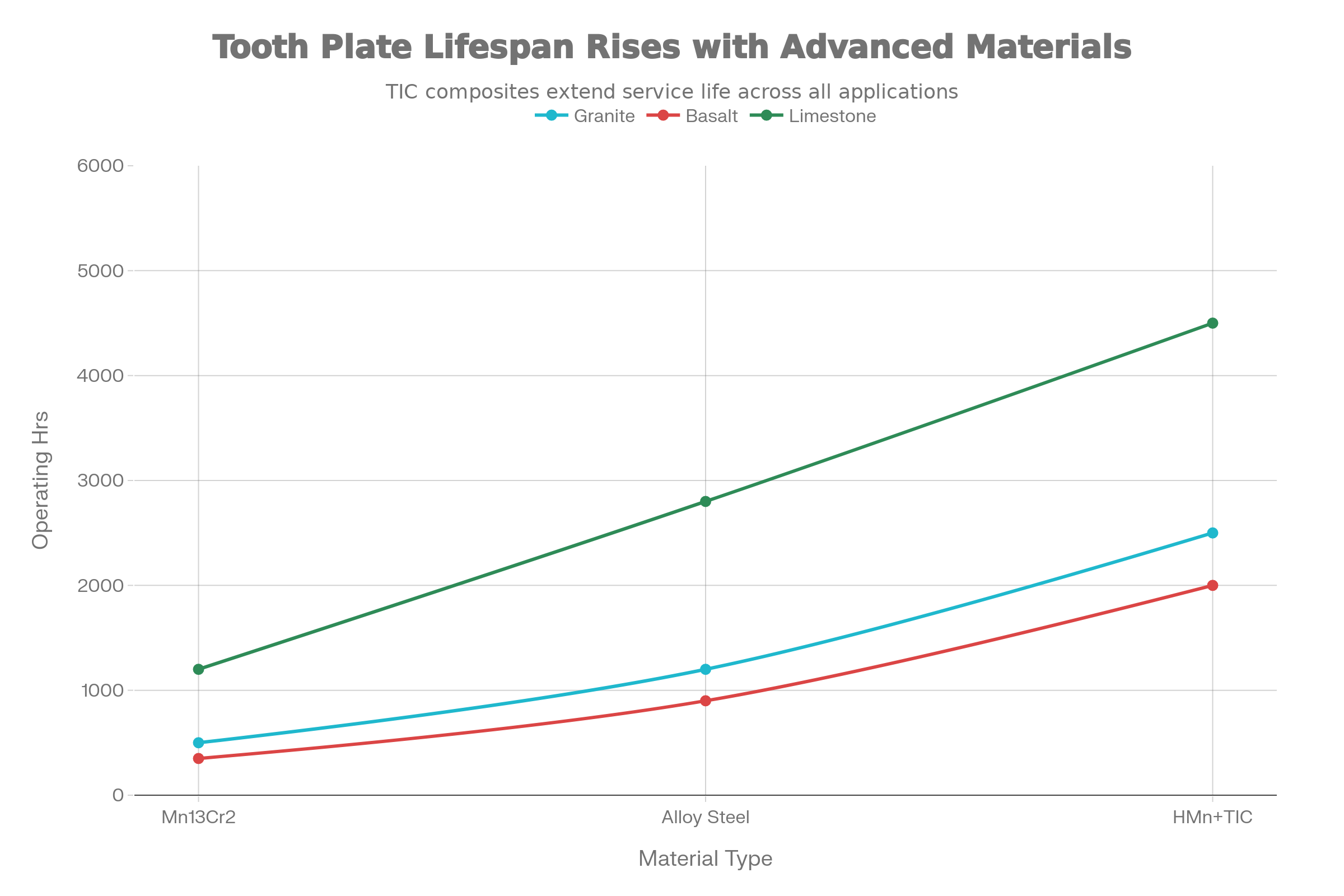
Empirical industry data establishes clear replacement interval guidelines across crushing applications, though actual intervals require customization based on specific operational factors including crusher design, feed characteristics, operating speed, and maintenance quality.
Granite and similar crystalline hard rocks present the most demanding jaw plate applications due to high Mohs hardness ratings (6-7) and angular particle geometry that produces aggressive grinding and chiseling wear. Standard manganese steel plates typically survive 3-4 months under normal operating conditions, translating to approximately 500 operating hours at typical 12-16 hour daily operation schedules. Premium alloy compositions extend intervals to 6-8 months, while specialized wear-resistant materials with TIC inserts can maintain performance for 10-14 months under equivalent operating intensity.
Basalt presents extreme hardness characteristics with dense crystalline structure that generates substantial compressive forces during fracture. Replacement intervals compress to 2.5-3 months under intensive operation, with operating hour budgets typically ranging from 350-400 hours before approaching critical wear thresholds. The homogeneous material characteristics allow less predictable wear patterns, with failure modes shifting from progressive wear to sudden catastrophic fracture when approaching replacement thresholds.
Limestone and similar sedimentary materials create the most forgiving operating environment, permitting extended plate intervals averaging 5-6 months at standard operating speeds. Extended intervals reflect reduced abrasive wear and lower compressive forces required for material fracture. However, limestone's higher moisture content and tendency toward material buildup within the crushing chamber create secondary wear mechanisms through corrosive attack and mechanical surface degradation from accumulated residue.
Accurate thickness measurement represents the foundational operational practice for determining optimal replacement timing. Rather than calendar-based replacement, quantitative measurement approaches enable data-driven decisions that prevent premature replacement while ensuring safe operational margins.
Equipment Requirements: Precision calipers or digital thickness gauges provide measurement accuracy within ±0.5mm, essential for identifying early wear trends and predicting replacement timing with two to four weeks advance notice. Ultrasonic measurement tools offer non-invasive alternatives for field assessment without requiring plate removal.
Measurement Frequency: Monthly thickness measurements establish reliable wear rate data, enabling predictive analytics that forecast replacement dates with 85-90% accuracy. Weekly measurements during intensive operations or high-wear applications provide more granular early warning capabilities.
Measurement Locations: Each jaw plate should be measured at minimum at four distinct locations: upper plate center, lower plate center, jaw corner regions, and transition zones between active crushing surfaces. Recording spatial wear distribution identifies uneven wear patterns requiring operational adjustments or rotation strategies.
Standard locking design: Replace when remaining thickness diminishes to 25-50mm depending on specific crusher model
Wedge retention systems: Replace at 20-25mm remaining thickness
Heavy-duty locking wedges: Permit operation to 60-65mm remaining thickness
Operating below these thresholds creates catastrophic failure risk as tooth root structure fails under compressive loads, potentially releasing plate fragments into the crushing chamber with attendant safety and equipment damage consequences.
Many modern jaw crusher designs incorporate reversible or rotatable plates that permit extended material utilization by accessing previously unused crushing surfaces. Strategic rotation represents one of the most cost-effective lifespan extension techniques, frequently delivering 50% additional operating life at zero material cost.
First Rotation Initiation: Execute plate rotation when lower plate wear reaches approximately 50% of original thickness, typically occurring at 5-7 months into service life depending on application severity. This timing ensures sufficient material thickness remains for secondary crushing phase.
Second Rotation Execution: Initiate second rotation when wear approaches 90% on rotated surface regions, typically 10-14 months after initial rotation, contingent on original material grade and application characteristics.
Documentation and Tracking: Maintain detailed rotation logs recording measurement dates, thickness values at rotation, operational hours, material tonnage processed, and wear rate calculations. This historical data enables precise lifespan prediction and optimal supplier sourcing decisions.
Rotation effectiveness depends critically on initial wear pattern characteristics. Symmetric wear distribution across upper and lower regions permits effective rotation, while highly localized wear concentrated in specific zones may limit rotation benefits to 20-30% lifespan extension. Uneven wear patterns frequently indicate operational issues including inadequate material distribution, incorrect crusher settings, or misalignment requiring correction before implementing rotation strategies.
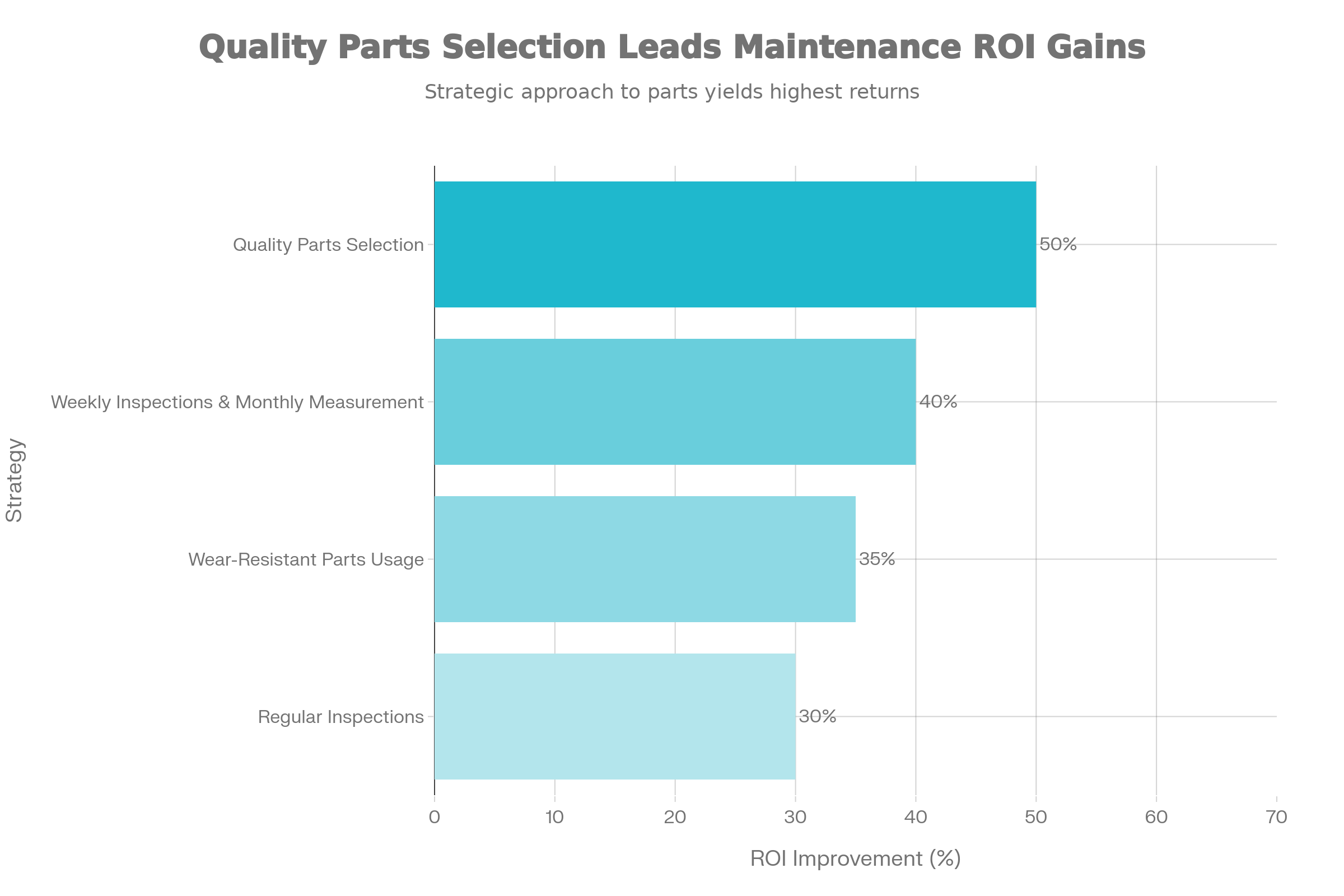
Maintenance ROI analysis demonstrates measurable financial returns from systematic preventive strategies, with implementation costs typically recovering through extended component life and reduced downtime within 2-4 months of operation.
Visual assessment of jaw plate crack initiation or chipping
Verification that safety guards remain intact and properly positioned
Lubrication system verification ensuring adequate bearing greasing
Fluid level checks for hydraulic systems and bearing oil supplies
Assessment of unusual noise patterns indicating bearing distress or bolt loosening
Early detection through daily inspection prevents minor issues from progressing to catastrophic failures, routinely preventing $25,000-100,000+ equipment repair costs.
Belt tension inspection and adjustment to factory specifications
Jaw plate rotation assessment and scheduling
Toggle plate wear evaluation and replacement timeline development
Closed-side setting (CSS) verification and adjustment to maintain design specifications
Complete bearing greasing according to manufacturer guidelines
Bolt tension verification across main frame, jaw mounting, and toggle assemblies
Operations implementing weekly maintenance protocols report 25% longer component life and 30% reduction in unplanned downtime compared to monthly-only approaches.
Precision thickness measurement using calipers with documentation of all measurement points
Visual assessment of wear pattern uniformity identifying operational adjustment needs
Bearing temperature monitoring and comparison against baseline readings
Liners and cheek plate evaluation for structural cracks or excessive material loss
Hydraulic system inspection for leaks, pressure consistency, and filter condition
Frame and pitman inspection for structural cracks or deformation
Monthly measurement data enables precise replacement timing prediction, allowing procurement 4-6 weeks in advance and scheduling replacement during planned maintenance windows that eliminate unplanned production interruptions.
While quantitative thickness measurement provides primary replacement guidance, visual damage characteristics often indicate replacement urgency independent of remaining material thickness.
Visible Cracks and Chipping: Crack initiation indicates material property degradation from accumulated fatigue damage and localized stress concentration. Progressive crack propagation creates catastrophic failure risk requiring immediate replacement regardless of remaining thickness, as fatigue cracks propagate exponentially during the final failure phase.
Exposed Base Metal or Oxidative Attack: Localized regions where protective surface layers have been abraded, exposing underlying base metal to oxidative attack, indicate advanced wear requiring prompt replacement. Oxidative corrosion accelerates material loss 3-5x compared to mechanical wear alone, particularly in humid or coastal environments.
Feed material characteristics represent one of the most significant variables influencing jaw plate lifespan, with proper material management potential to extend component life by 30-40% compared to suboptimal practices.
Hard, Abrasive Materials: Granite, quartzite, and similar crystalline materials demand premium plate selections with enhanced wear resistance. Operating with undersized or softer materials than design specification wastes material capability while increasing costs.
Oversized Feed Material: Rocks exceeding 80% of crusher opening create concentrated impact loads on specific jaw plate regions, producing localized wear hotspots that concentrate 50-70% of wear damage in narrow zones. Pre-screening equipment to remove oversized material prevents this catastrophic wear concentration.
Moisture Content and Sticky Materials: High moisture materials create chamber buildup, increasing stress on crushing surfaces and promoting oxidative corrosion. Pre-drying equipment or pre-screening to remove fines prevents material accumulation and extends plate life by 20-30%.
Even Material Distribution: Uniform feed distribution across the crushing chamber's full width ensures symmetric wear pattern development, permitting effective plate rotation. Concentrated feeding to specific points creates asymmetric wear patterns that reduce rotation effectiveness from potential 50% extension to 20% or less.
Selection of casting jaw crusher tooth plate suppliers profoundly impacts both initial cost and total cost of ownership through material quality, dimensional accuracy, and post-sale support capabilities.
Certification and Quality Systems: ISO 9001 certification indicates systematic quality control throughout production, material verification, and dimensional accuracy. Reputable suppliers maintain third-party laboratory testing of material composition and mechanical properties.
Material Documentation: Request comprehensive material composition reports, mechanical property test certificates, and batch traceability documentation. Premium suppliers provide detailed chemical composition analysis, tensile strength verification, and hardness certification for each production batch.
Lead Time and Inventory: Evaluate supplier lead times (typically 20-50 days for quality aftermarket suppliers, 25-40 days for specialized alloys) and establish inventory relationships ensuring replacement availability without extended downtime. Strategic suppliers offer expedited delivery options for emergency replacement scenarios.
Warranty and Support: Effective warranty structures extend 6-12 months minimum, covering manufacturing defects and performance failures. Premium suppliers offer technical support including compatibility verification, installation guidance, and performance optimization consultation.
Compatibility Verification: Request model-specific compatibility documentation confirming dimensional accuracy, tooth pattern specifications, and retention system compatibility. Dimensional discrepancies create fitting issues and performance degradation.
OEM plates guarantee perfect fit and precision engineering but typically command 30-70% price premiums over quality aftermarket alternatives. Quality aftermarket suppliers from reputable manufacturers offer comparable performance at substantially lower cost when sourced from ISO 9001 certified producers with documented material traceability and comprehensive testing.
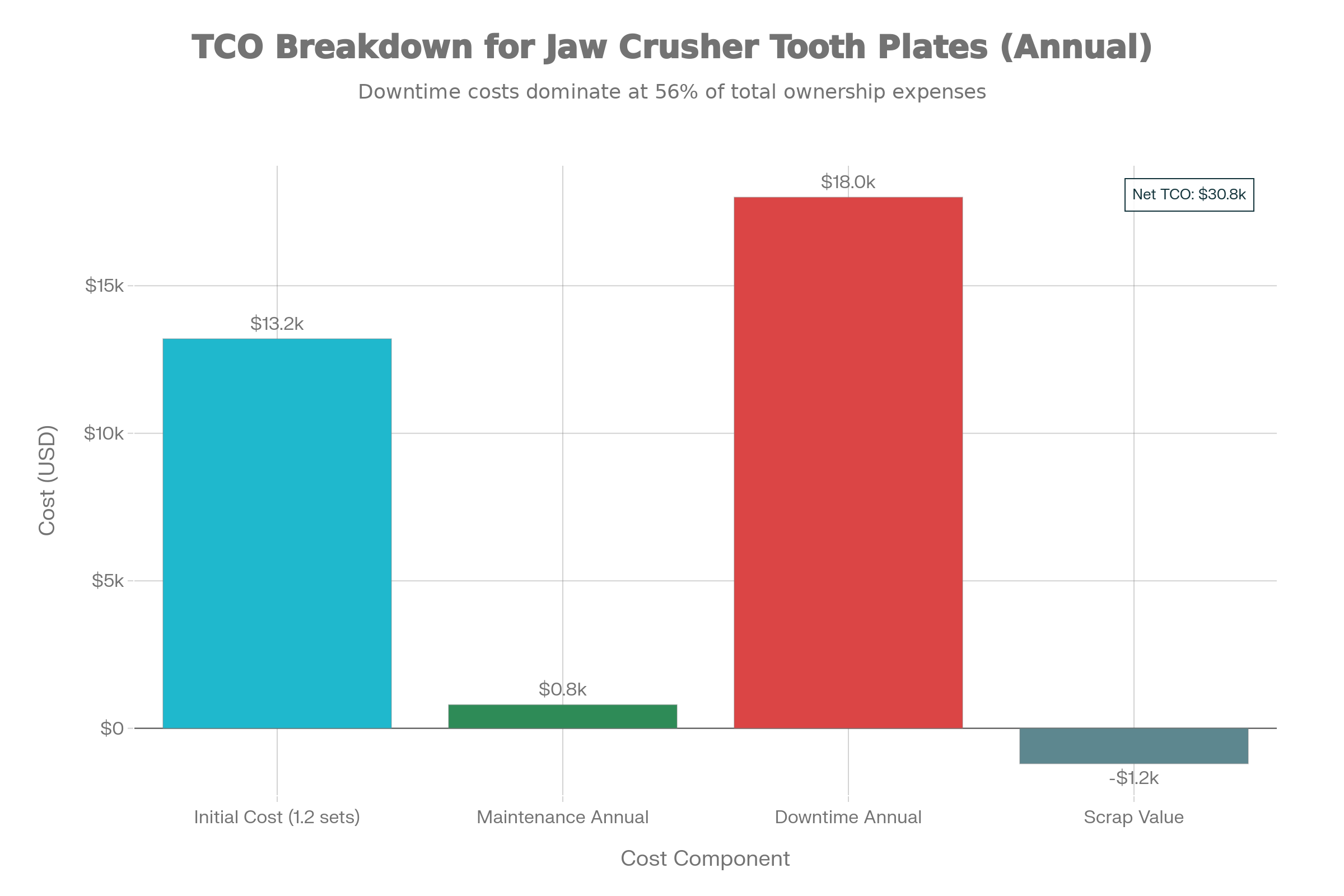
Comprehensive total cost of ownership analysis informs supplier selection and material grade decisions by comparing purchase price against operational expenses and downtime risks:
For a typical mining operation crushing 200 tons per hour requiring 1.2 replacements annually with $11,000 plate costs, $800 annual maintenance, and $18,000 downtime costs, annual total cost reaches approximately $39,400 when accounting for $1,200 scrap value recovery.
Investment in premium wear-resistant materials at 50-70% additional purchase cost typically delivers 5-10 year ROI through reduced replacement frequency and downtime costs. Operations with downtime costs exceeding $20,000 per hour achieve positive ROI within 2-3 months of extended plate life.
Maximizing jaw crusher tooth plate lifespan requires integrated approaches combining quantitative thickness monitoring, strategic rotation implementation, daily and weekly maintenance discipline, optimal feed material management, and deliberate supplier partnerships with quality-focused providers. Equipment operators implementing comprehensive maintenance protocols routinely achieve 30-50% lifespan extension compared to reactive approaches, translating to annual cost reductions of $15,000-30,000+ for mid-sized operations while substantially improving operational reliability and productivity.